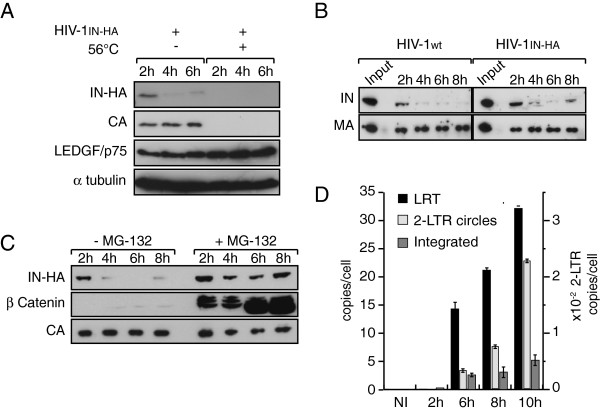
Figure 1.
IN is rapidly degraded in a proteasome-dependent manner during early steps of HIV-1 replication. (A) SupT1 cells were infected with HIV-1IN-HA or heat-inactivated virus (56°C). At indicated time post infection, cells were lysed and equivalent amounts of each sample (100 μg of protein) were analyzed using Western blotting with antibodies against HA, CA, LEDGF/p75 and α-tubulin as loading control. (B) Both IN-HA and non-tagged IN are rapidly degraded following viral entry into the cell. SupT1 cells were infected with HIV-1IN-HA or HIV-1wt. At indicated time post infection, cells were lysed and equivalent amounts of each sample (100 μg of protein) were analyzed using Western blotting with antibodies against IN and MA. Input represents 0.1& of the amount of virus used to infect the cells. (C) IN is targeted to proteasomal degradation following infection of the cells. SupT1 cells were infected with HIV-1IN-HA in absence or presence of proteasome inhibitor MG-132. As in (B), cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against HA, β-Catenin and CA. β-Catenin was used as a control to monitor the efficiency of MG-132 treatment. (D) Proviral integrated DNA is readily detected at 6 h p.i. SupT1 cells were infected with HIV-1IN-HA, and DNA was extracted at indicated time post infection. Late reverse transcription product (LRT), 2-LTR circles and integrated viral DNA were quantified by real time PCR.