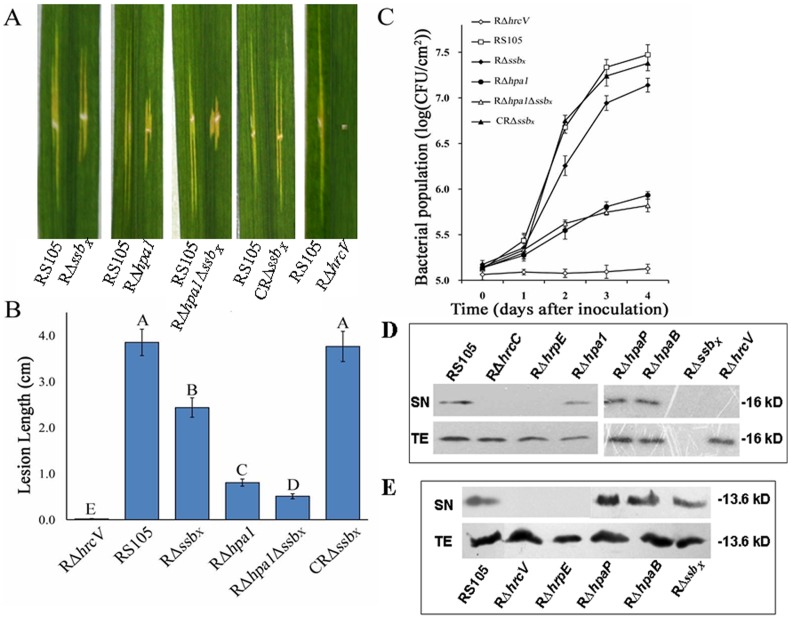
Figure 6. Secretion of SSBXoc depends on the T3SS and is required for full virulence and bacterial growth in rice.
(A) Symptoms and (B) lesions lengths were used to assess the virulence of X. oryzae pv. oryzicola RS105 and selected mutants. One half of a rice leaf (IR24, two-months old) was inoculated with wild-type RS105, and the remaining half was inoculated with one of the following deletion mutants: ssbXoc deletion mutant RΔssbX, hpa1 mutant RΔhpa1, the double mutant RΔssbXΔhpa1, the complemented mutant CRΔssbX, and the T3SS mutant RΔhrcV. Ten leaves were inoculated with each strain (OD600 = 0.3; approximately 3×108 cfu/ml) by leaf-needling, and the assay was conducted in triplicate. Bacterial leaf streak symptoms were photographed 14 dpi, and representative symptoms are shown (A). The average lesion lengths formed by the wild-type and mutants were measured 14 dpi (B), and data represent means ± SD from three replicates. Different letters in each data column indicate significant differences at P = 0.01 (t test). (C) Bacterial growth assays in planta. Strains (OD600 = 0.3) were infiltrated into leaves of rice seedlings (IR24, two-weeks old) with blunt-end plastic syringes, and the cfu/cm2 of tissue was evaluated as described in Methods. Data represent means ± SD from three replications. (D) and (E) demonstrated the secretion of SSBXoc (D) and Hpa1 (E) are dependent on a functional T3SS of X. oryzae pv. oryzicola. This experiment utilized X. oryzae pv. oryzicola RS105 and strains containing mutations in the following genes: hrcV (RΔhrcV), hrcC (RΔhrcC), hrpE (RΔhrpE), hpaB (RΔhpaB), hpaP (RΔhpaP), hpa1 (RΔhpa1) and ssbXoc (RΔssbX) to express ssbXoc-c-myc or hpa1-c-myc fusion (as a positive control). After incubation (8 h) in hrp-inducing medium XOM3, total cell extracts (TEs) and culture supernatants (SNs) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with an anti-c-Myc antibody. The immunoblotting assay was conducted twice, and similar results were obtained each time. For the detection of SSBXoc, the strain RΔssbX with the empty vector pUFR034 was used as a negative control (D).