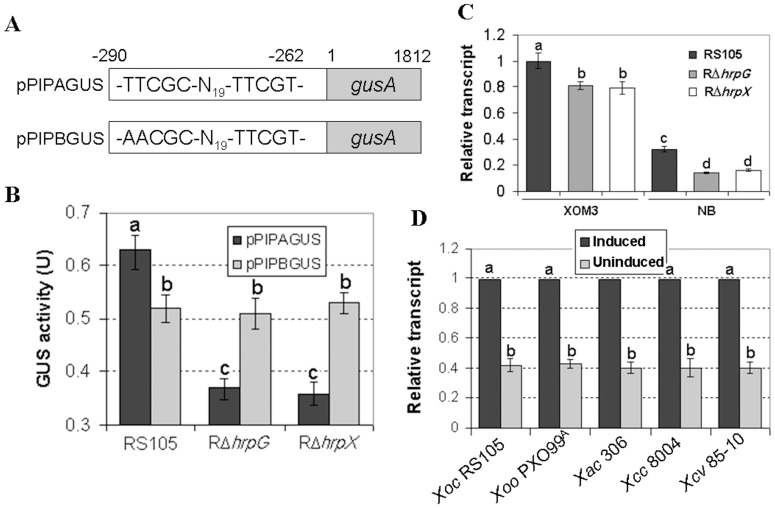
Figure 7. ssbX is expressed in hrp-inducing conditions and regulated by HrpG and HrpX.
(A) Schematic map of a transcriptional fusion where the ssbXoc promoter of X. oryzae pv. oryzicola RS105 is fused to the gusA reporter gene. Upper panel shows pPIPAGUS containing the ssbXoc promoter and an imperfect PIP-box (TTCGC-N19-TTCGT) fused with a promoter-less gusA gene. Lower panel shows pPIPBGUS with a mutated ssbXoc promoter (the first TT nucleotides replaced with AA) fused with gusA. (B) â-glucuronidase (GUS) activity in the hrp-inducing medium XOM3. Plasmids pPIPAGUS and pPIPBGUS were transferred into the wild-type RS105 and mutants RΔhrpG and RΔhrpX. The recombinant strains were then grown in hrp-inducing medium XOM3 for 16 h. GUS activity was determined by measuring the OD at 415 nm using ρ-nitrophenyl-â-D-glucuronide as a substrate. Data represent the mean ± SD of triplicate measurements. The different letters above each horizontal column indicate significant differences at P = 0.01 (t test). (C) Expression of ssbXoc in hrp-inducing and nutrient-rich media. Real-time quantitative RT-PCR was used to compare relative expression of ssbXoc in X. oryzae pv. oryzicola strains RS105, RΔhrpG, and RΔhrpX. RNA was isolated from strains grown in a nutrient-rich medium (NB) and the hrp-inducing medium (XOM3) for 16 h. The relative mRNA levels of ssbXoc in the hrpG and hrpX mutants were calculated with respect to the wild-type strain. Values given are the means ± SD of triplicate measurements from a representative experiment, and similar results were obtained in two other experiments. Different letters above horizontal columns represent significant differences at P = 0.01 using the Student’s t test. (D) Real-time RT-PCR evaluation of ssbX expression in Xanthomonas species. Strains were grown at 28°C for 16 h in NB or one of the following hrp-inducing media: XOM3 for X. oryzae pv. oryzicola RS105 and X. oryzae pv. oryzae PXO99A (Xiao et al. 2007), XVM2 for X. axonopodis pv. citri 306 & X. campestris pv. vesicatoria 85-10, and MMX for X. campestris pv. campestris 8004 (see methods). Relative mRNA quantitative of ssbX was calculated with respect to the levels observed for wild-type strains grown in NB. Genes encoding 16S rRNA were used as internal controls. Data represent means ± SD of triplicate measurements (P = 0.01, t test).