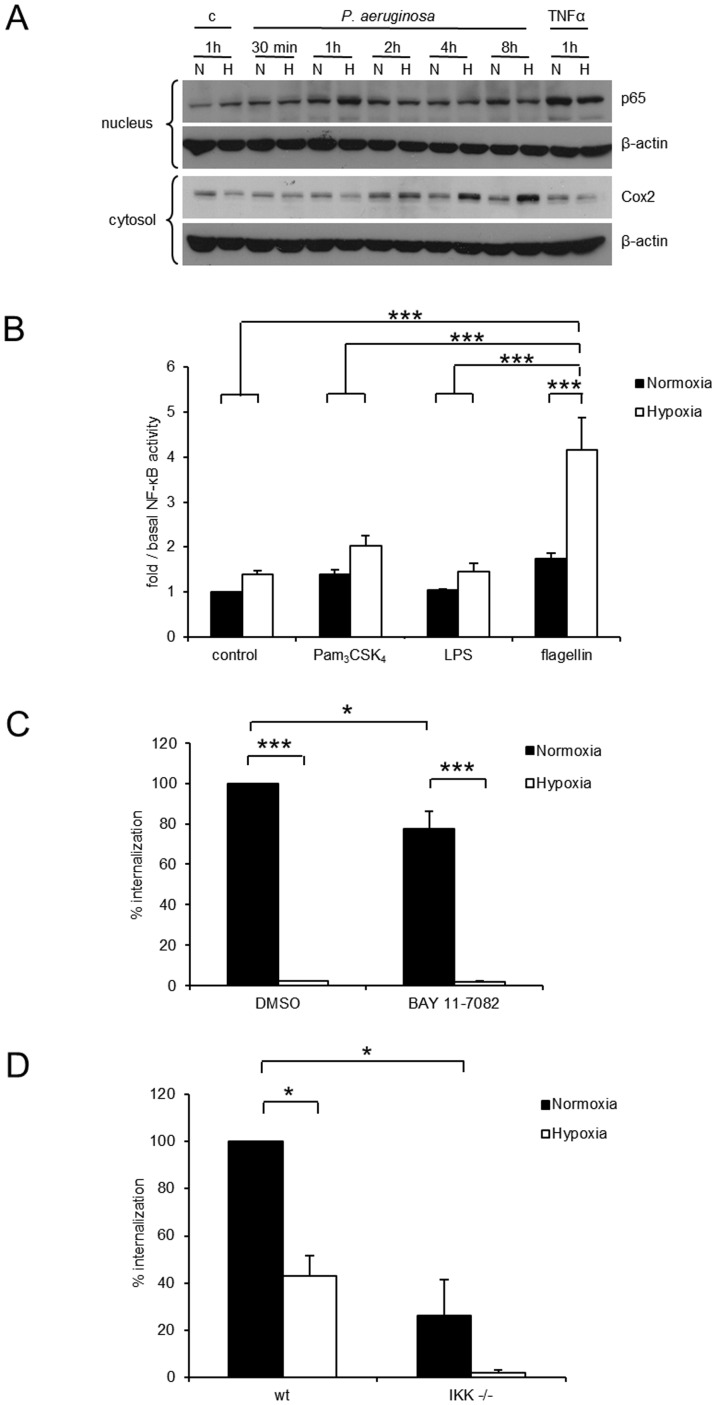
Figure 3. Hypoxia increases NF-κB activity in response to P. aeruginosa but silencing of NF-κB fails to normalize hypoxia induced decreased internalization.
A: Protein levels of nuclear p65 and cytosolic Cox2 were investigated by immunoblot in A549 cells stimulated with heat inactivated P. aeruginosa in normoxia (N) and hypoxia (H) for the indicated times. B: NF-κB transcription factor activity was measured by a NF-κB luciferase reporter assay in normoxic and hypoxic A549 cells stimulated with TLR ligands for TLR2 (Pam3CK4, 2 µg/ml), TLR4 (LPS, 0.5 µg/ml) and TLR5 (flagellin, 0.5 µg/ml). Data represent mean ± SEM of 6 independent experiments (*** p<0.0001). C: Intracellular P. aeruginosa in A549 cells in normoxia or hypoxia in the presence or absence of the NF-κB inhibitor BAY 11-7082 (10 µM) or its solvent DMSO were determined in an antibiotic protection assay. Data represent mean ± SEM of 4 independent experiments (* p<0.05, *** p<0.0001). D: Antibiotic protection assay with P. aeruginosa in MEF wt and IKK−/−cells under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Data represent mean ± SEM of 2 independent experiments (* p<0.05).