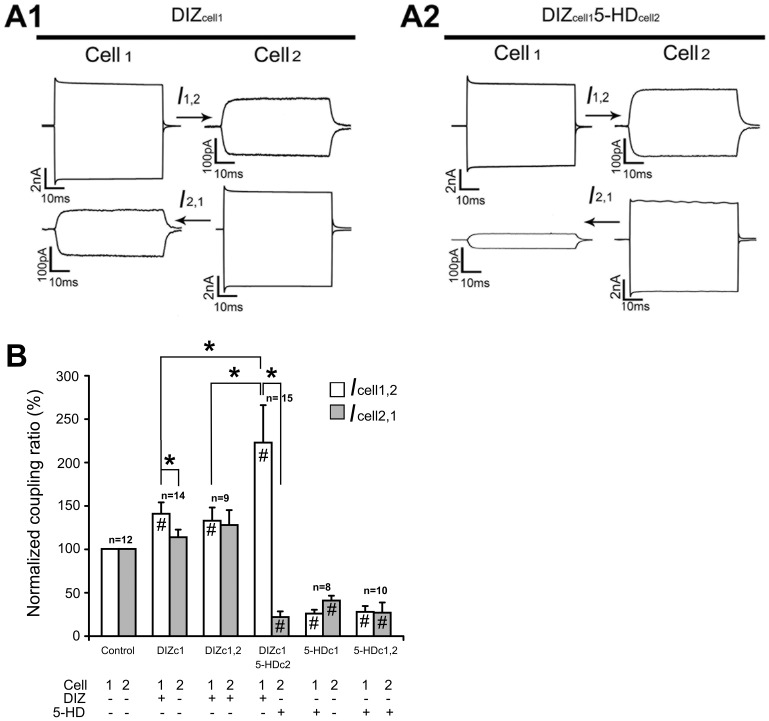
Figure 4. Activation of mitoKATP channels in single astrocyte increased the electrical coupling of directly coupled astrocytes in slices.
Internal solution containing test drugs was used to diminish the pharmacological effects induced by opening/blocking neuronal KATP channels in slice. (A) Representative electrical coupling trace of a recorded astrocyte pair after addition of DIZ in cell1 (A1), and after addition of DIZ in cell1 and 5-HD in cell2 for 5 min (A2). (B) Bar graph shows that compared to that observed in DIZ-treated slices, we did not find any differences in coupling ratios with the internal solution containing DIZ at 5 min. Interestingly, the level of coupling ratios from the Scell with DIZ-contained internal solution (Scell-DIZ) to the Rcell with normal internal solution (Rcell-) was higher than that from the Scell with normal internal solution (Scell-) to the Rcell with DIZ-containing internal solution (Rcell-DIZ). Moreover, the level of coupling ratios from the Scell- to the Rcell with 5-HD-containing internal solution (Rcell-5-HD) was higher than that from the Scell with 5-HD-containing internal solution (Scell-5-HD) to the Rcell-, even though the differences in the ratios were not significant. When Scell-DIZ was combined with Rcell-5-HD in our experiments, this elevation in coupling ratios became significant, as the level increased by 58% and 68% than that from Scell-DIZ to Rcell- and Scell-DIZ to Rcell-DIZ respectively. These results were determined from paired astrocyte recordings at interastrocytic distances of 20 – 40 µm. Mean ± SEM; * P<0.05. # P<0.05 compared to the control. DIZ, Diazoxide; 5-HD, 5-hydroxydecanoate; Rcell, recipient cell; Scell, stimulated cell.