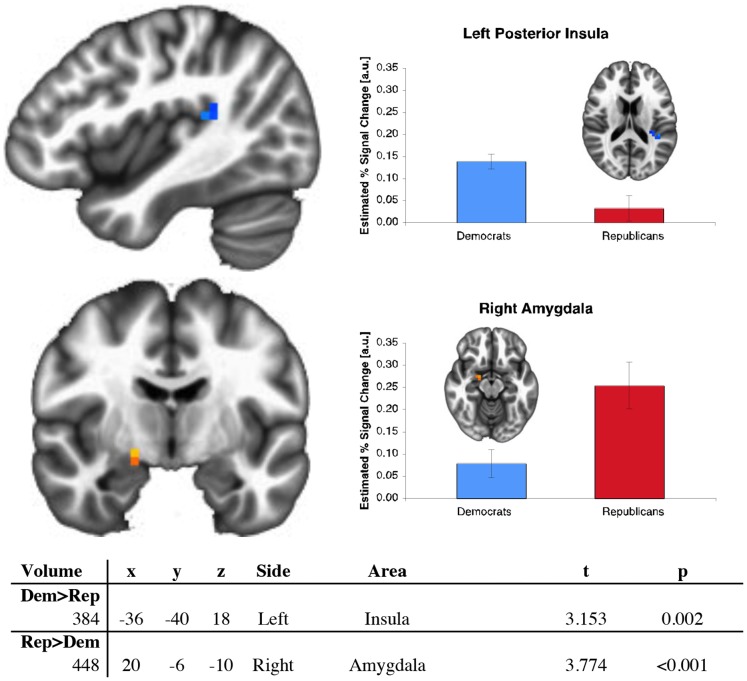
Figure 1. Republicans and Democrats differ in the neural mechanisms activated while performing a risk-taking task.
Republicans more strongly activate their right amygdala, associated with orienting attention to external cues. Democrats have higher activity in their left posterior insula, associated with perceptions of internal physiological states. This activation also borders the temporal-parietal junction, and therefore may reflect a difference in internal physiological drive as well as the perception of the internal state and drive of others.