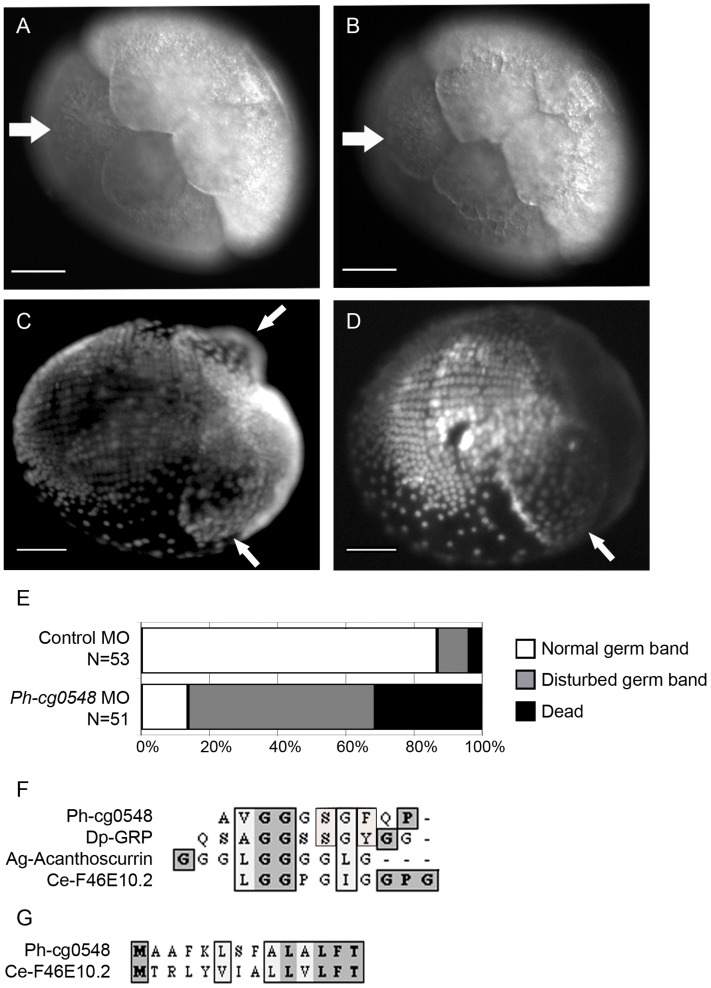
Figure 5. Functional analysis of cg1295 and cg0548 by knockdown experiments.
(A, B) In vivo imaging of an siRNA-injected embryo (200 µM Stealth-RNA, 1-cell stage microinjection) imaged at 6 hpi (A) and 6,5 hpi (B). The white arrow in (A) indicates the site of the missing micromere cell after incomplete third cleavage. The same embryo was imaged 30 min later (6,5 hpi, B). The white arrow indicates the micromere cell that has just formed after a delayed division of one blastomere cell from the 4-cell stage. The changing shape of the other blastomeres at 6,5 hpi is a sign of initiated fourth cleavage (from 8- to 16-cell stage). Scale bar corresponds to 100 µm. (C) A ventro-lateral view of a DAPI-stained, control morpholino injected embryo fixed at 5 dpi. The white arrows indicate the position of the midgut anlagen (disc-shape structures). The ectodermal cell rows are clearly visible on the posterior ventral side of the embryo. (D) A ventro-lateral DAPI view of a anti-cg0548 morpholino-injected embryo fixed at 5 dpi. The white arrow indicates the single disc-shape structure in the anterior part, whereas the second one is missing. (E) Phenotype scoring and survival of control and anti-cg0548 morpholino-injected embryos at 5 dpi. More than 80% of the control embryos show normal germ band formation. In contrast, only 15% of the anti-cg0548 morpholino-injected embryos were developing normal and 30% were already dead at the observed time point. (F) The cg0548 RNA is coding for a small glycine-rich protein. The protein sequence includes 11 tandem repeats of the sequence Ala-Val-Gly-Gly-Gly-Ser-Gly-Phe-Gln-Pro (AVGGGSGFQP). Possible homologs of Ph-cg0548 were found in a wide range of organisms (from the closely related Daphnia pulex to the worm Caenorhabditis elegans). These proteins have short amino acid sequence (several hundred residues) and glycine-rich tandem repeats. Alignment of the repetitive element shows that Parhyale and Daphnia share the highest similarity, including a serine and an aromatic residue (F/Y). The position of the proline residue is shared between Parhyale and C. elegans. (G) Sequence alignment of the non-repetitive N-terminal part of the protein shows that C. elegans and Parhyale both have a stretch of aliphatic residues and a conserved phenylalanine, followed by a threonine.