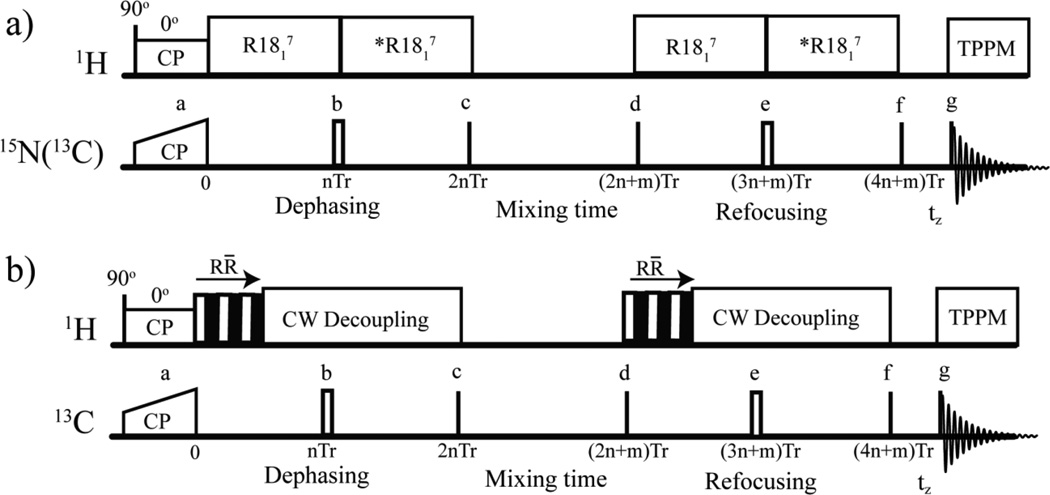
Figure 1.
The R-CODEX pulse sequences used in these studies to detect conformational exchange rates (a) and reorientation angles (b). 90° pulses are denoted using black lines, and 180° pulses are represented by hollow rectangles. The 180° pulse in the middle of dephasing and refocusing periods refocuses the dephasing due to the isotropic chemical shift. CP: cross polarization. Tr: Rotor period. *R1871: R1817 with 180° phase shift to prevent averaging of the recoupled dipolar coupling by 180° pulse. The mixing time should be an integral number of rotor periods [7]. The dephasing and refocusing periods should be even multiples of the rotor periods to reduce net evolution of other anisotropic interactions. In (b), the mixing time was fixed while the number of R̄R blocks (denoted by one hollow (R) and one solid (R̄) square) of the R1871 pulse was increased systematically. All phases represented by a-g are given in the supplemental materials.