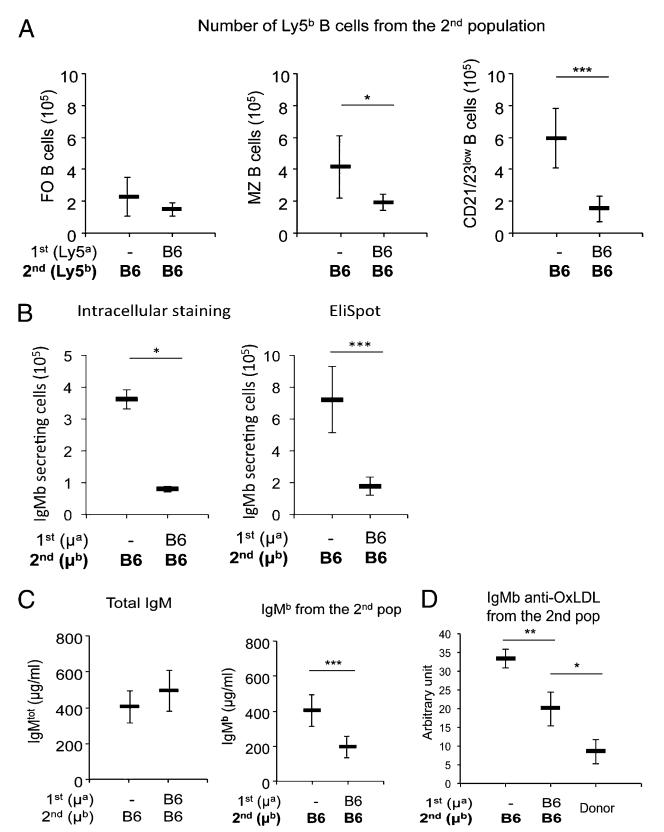
FIGURE 2.
Sequential B cell transfers. (A) Shows the number of FO CD21int/highCD23high (left panel), MZ CD21highCD23low (middle panel), and CD21lowCD23low cells (right panel) recovered from the second Ly5bIgHb population when injected alone (left) or into mice injected 4 wk before with a first Ly5a IgHa cell population. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of values for nine individual mice. Note that whereas the number of resting B cells was not altered, the number of CD21highCD23low and CD21lowCD23low cells present among the second set of B cells was significantly lower when these cells were transferred into host mice already injected with a first set of B cells. (B) Shows the number of IgMb-secreting cells by the second B cell population when transferred into naive hosts (left) or into a host containing a first B cell population accessed by intracytoplasmic staining (left panel) or by Ig secretion (ELISPOT) (right panel). Each bar represents the mean ± SD of values for four to five individual mice. (C) Shows the quantity of IgMb produced by the second B cell population when transferred into naive hosts (left) or into a host containing a first B cell population. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of values for nine individual mice. Note the significantly reduced IgM production by the second B cell population when these cells were transferred into mice containing a first set of B cells transferred 4 wk before (right). Note that the total IgM concentrations were slightly greater in mice injected with two B cell populations than in the mice injected with the first population only (left). Similar results were obtained in five independent experiments or when the order of injection of the two B cell populations was inverted. Statistically significant differences are shown. (D) Shows the titers (expressed in arbitrary units/unit of IgMb) of self-reactive IgMb anti-mouse OxLDL produced by the second B cell population when transferred into naive hosts (left) or into a host containing a first B cell population (middle). For comparison, the titers of self-reactive IgMb anti-mouse OxLDL in the serum of donor B6 mice are shown (right). The sera of the different mice were normalized so that we can compare the titers of self-reactive IgMs present for the same amount of total IgMb concentration of the different mice. Note the selective reduction of anti-mouse OxLDL self-reactive Abs secreted by the second B cell population when these cells were transferred into mice containing a first set of B cells. Statistically significant differences are shown. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.