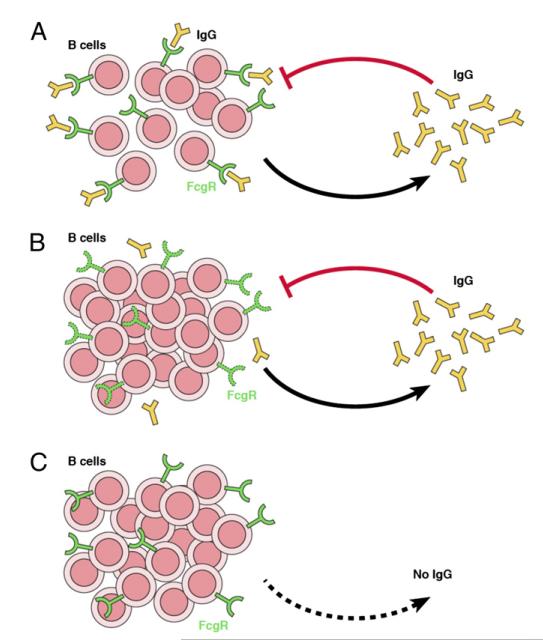
FIGURE 5.
(A) Quorum sensing: the presence of soluble IgG and the ability of the B cells to detect its levels are crucial to the homeostasis of the immune system. Quorum sensing: the IgG secreted by activated B cells is detected (sensed) by the inhibitory FcγRIIB expressed by B cells that prevents further B cell activation. That is to say: overall B cell populations adapt their behavior according to the sensing of the quantities of IgG produced. (B) Failure of quorum sensing by defective sensor molecule: the inability to detect soluble IgG because of defects in the FcγRIIB expression (in FcγRIIB−/− mice) or signaling (in SHIP1−/− mice) leads to hyper-IgM syndromes and autoimmune disease. (C) Failure of quorum sensing by absence of the sensed molecule IgG also leads to hyper-IgM syndromes and autoimmune pathology.