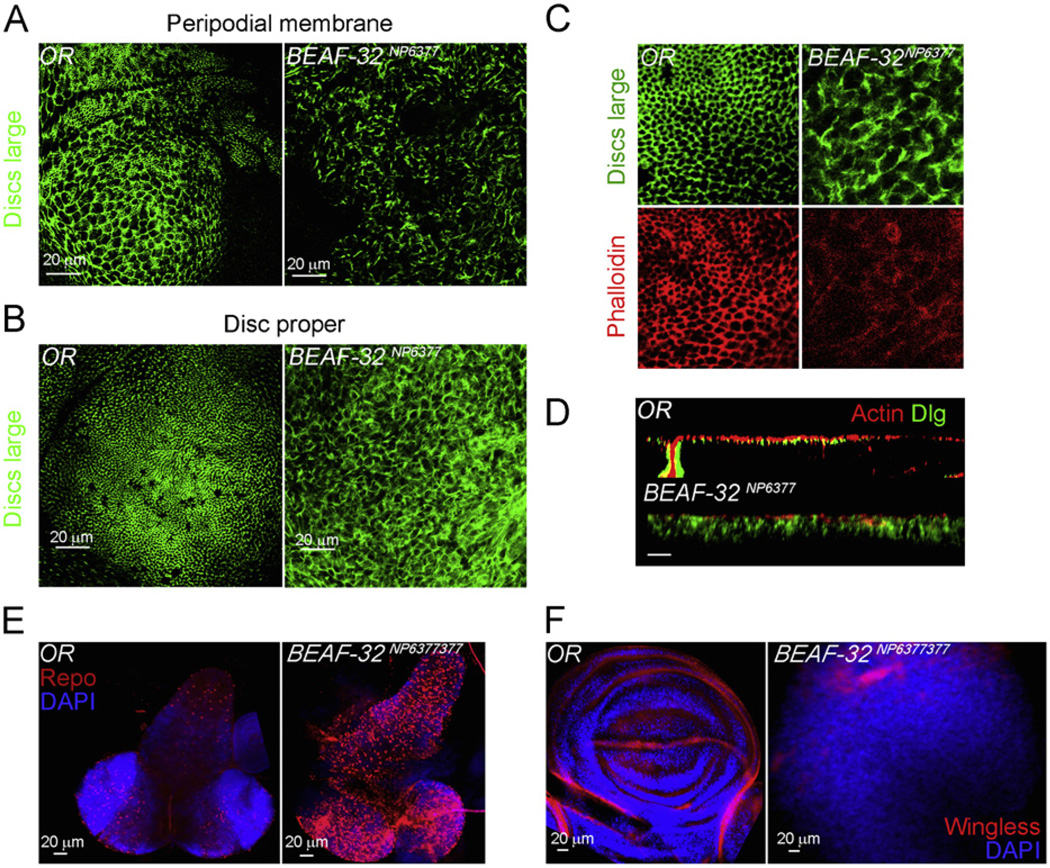
Fig. 2.
BEAF-32 mutants show loss of epithelial architecture and defects in patterning and cell differentiation. (A) Immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies to the Discs Large (Dlg) protein (green) in the wing imaginal tissue of wild type and BEAF-32NP6377 mutant larvae. The panels show the projections of confocal sections from the peripodial membrane. (B) Same as in (A) but showing the disc proper cells in the wing pouch. (C) The adherens junctions marked by the Dlg protein (green) and actin marked by pholloidin (red). (D) Longitudinal cross section (X–Z) of wing epithelium in the pouch region of the wing imaginal disc; actin in red marks the cytoskeleton and Dlg in green marks adherent junctions. (E) The central nervous system from wild type and mutant larvae stained with the glial cell marker Repo (red) and DAPI (blue). Wing imaginal tissues stained for wingless (red) showing the dorso-ventral boundary in wild type discs and its absence in the mutant; DAPI stains DNA (blue). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)