Figure 8.
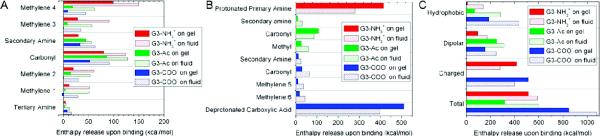
Enthalpy release from the interaction of the dendrimer with the lipids is shown for various parts of the dendrimer. For the inner dendrimer moieties shown in Figure 4, the enthalpies of interaction for each moiety type are shown in (A). For each moiety found within the dendrimer terminations, as shown in Figure 1, the enthalpies of interaction are shown in (B). The results of (A) and (B) are combined into (C) as the dendrimer moieties are categorized as hydrophobic, dipolar, or charged. The charged moieties less strongly bound to the fluid vs gel phase lipids where as the hydrophobic moieties bind over twice as strongly. The majority of the fluid vs gel phase lipid binding differences is mediated by the hydrophobic dendrimer components.
