Figure 4. Effects of IFN-I on dendritic cell subsets.
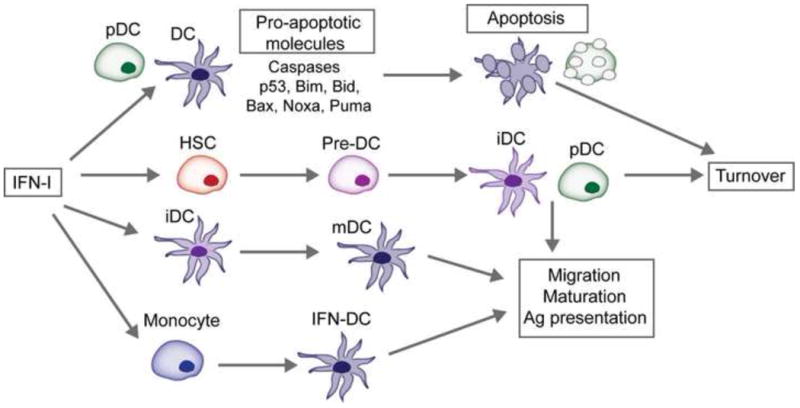
IFN-I promote the migration, maturation and antigen (Ag) presenting capabilities of DCs. IFN-I also induces the differentiation of monocytes into a specialized subset of DC called interferon-induced DC (IFN-DC). Recent evidence suggests that IFN-I regulates DC turnover. Both splenic cDCs and pDCs upregulate caspases and molecules involved in the intrinsic apoptosis pathway following exposure to IFN-I. Furthermore, dormant hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) are activated by IFN-I to proliferate and differentiate which may replace activated or dying DCs during antiviral responses. The regulated turnover of cDCs and pDCs during IFN-I-mediated responses may be a mechanism to prevent excessive immune stimulation and immunopathology. iDC, immature DC; mDC, mature DC.
