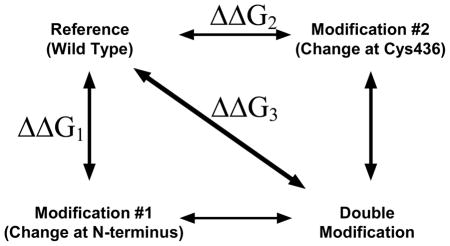
Table 4.
Additivity of mutant cycles
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | Modification #1 | Modificaiton #2 | Double modification | |||||||
| Ka-PEP [mM] | Modification description | Ka-PEPb [mM] | ΔΔG1a (kcal/mol) | Modification description | Ka-PEP [mM] | ΔΔG2a (kcal/mol) | Calculated ΔΔG1 + ΔΔG2 (kcal/mol) | Ka-PEP [mM] | Δ ΔG3a (kcal/mol) | |
| Wild Type | 0.240±0.002 | Δ2–10 | 0.605±0.004 | 0.55±0.01 | C436S | 0.802±0.004 c | 0.726±0.008 | 1.28±0.02 | 1.139±0.003 | 0.938±0.007 |
| C436N | 0.703±0.004 c | 0.647±0.008 | 1.20±0.02 | 1.016±0.005 | 0.869±0.008 | |||||
| S12D | 0.552±0.007 | 0.50±0.01 | C436S | 0.802±0.004 c | 0.726±0.008 | 1.23±0.02 | 0.89±0.01 | 0.79±0.01 | ||
| C436N | 0.703±0.004 c | 0.647±0.008 | 1.15±0.02 | 0.95±0.01 | 0.83±0.01 | |||||
| C338A | 0.93±0.01 | 0.82±0.01 | 1.32±0.02 | 2.09±0.02 | 130±0.01. | |||||
ΔG = change in free energy associated with PEP binding. ΔΔG = the difference in ΔG of PEP binding of modified protein relative to that of the wild type enzyme. Conversion of Ka-PEP to ΔG is based on the generally accepted view that PYK isozymes function as rapid equilibrium systems (30). As such, the free energy associated with PEP binding was calculated by ΔG=−RTln Ka-PEP.
values from (12)
values from Table 2
