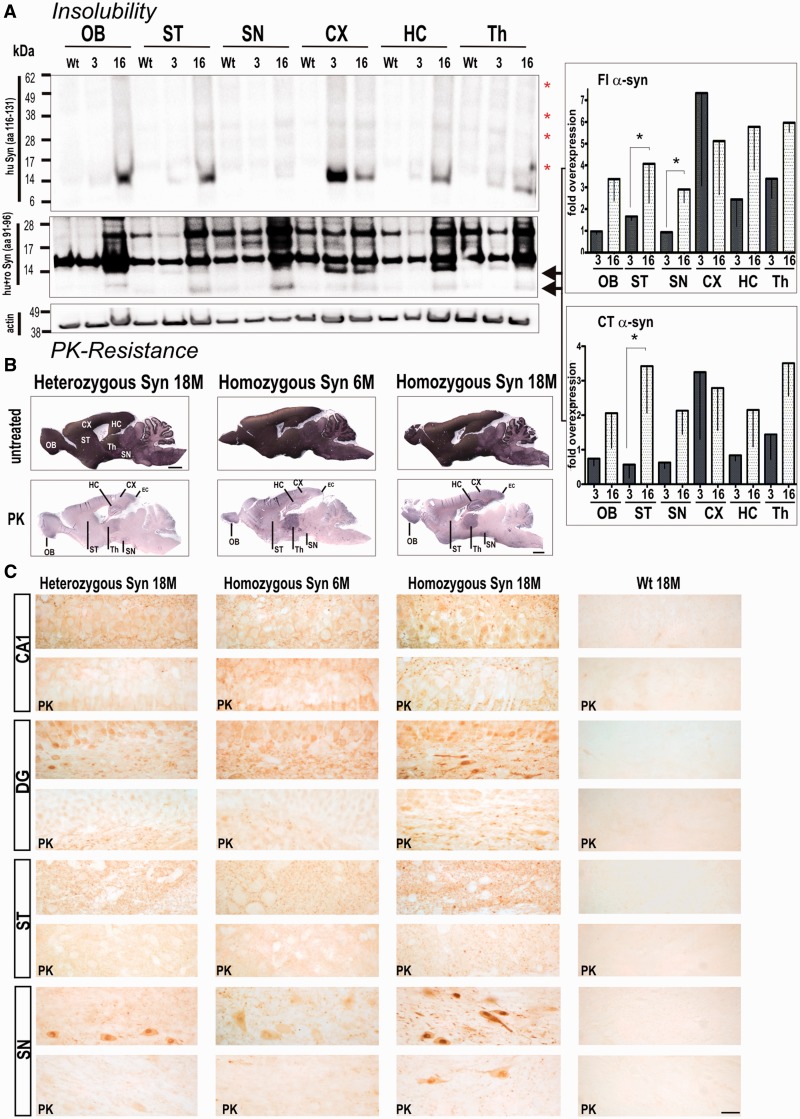
Figure 2.
Accumulation of proteinase K (PK) resistant and insoluble full-length (FL) α-synuclein is age- and gene-dosage dependant with insoluble full-length (Fl) α-synuclein and C-terminal truncated α-synuclein significantly enriched in striatum. (A) Brains of 3- and 16-month-old rats were sequentially extracted and the final pellet resolved in 8 M urea and 5% SDS. Analysis of α-synuclein insolubility showed a marked increased of monomeric full-length α-synuclein, and the typical high molecular smear of SDS promoted breakdown of aggregated α-synuclein species in 16-month-old transgenic rats (Syn) when using C-terminally localized 15G7 antibody (red asterisks). Consistently, detection with syn1 antibody (aa 91–96) revealed an increase in insoluble full-length α-synuclein and C-terminal truncated α-synuclein in aged animals. Syn1 antibody also detected α-synuclein unspecific bands at ∼17 and 28 kDa in both wild-type control rats and BAC synuclein transgenic rats. Band intensities were quantified, normalized to β-actin and then to control expression level and expressed as x-fold overexpression (–SEM) relative to 16-month-old wild-type control rats. Bar graphs represents means of n = 3 animals per group of three independent blots. *P < 0.05. (B) Representative images of abundant proteinase K-resistant fibres detected in several brain regions of BAC synuclein transgenic rats. Heterozygous BAC synuclein transgenic rats (18-month-old, 18 M) and 6-month-old (6 M) homozygous rats were used as additional controls to evaluate the increase of human α-synuclein positive fibres. (C) Proteinase K treatment diminished α-synuclein reactivity in both neuronal cell soma and neuropil of heterozygous and young homozygous animals, whereas proteinase K resistant α-synuclein immunoreactive granules were observed in neuropil of the CA1 and striatum and in the perinuclear region of neurons of the dentate hilus and substantia nigra. Scale bars: upper panels = 3 mm in (in situ stained overviews); lower panels = 20 µm. OB = olfactory bulb; CX = cortex; DG = dentate gyrus; HC = hippocampus; SN = substantia nigra; ST = striatum; Th = thalamus; wt = wild-type.