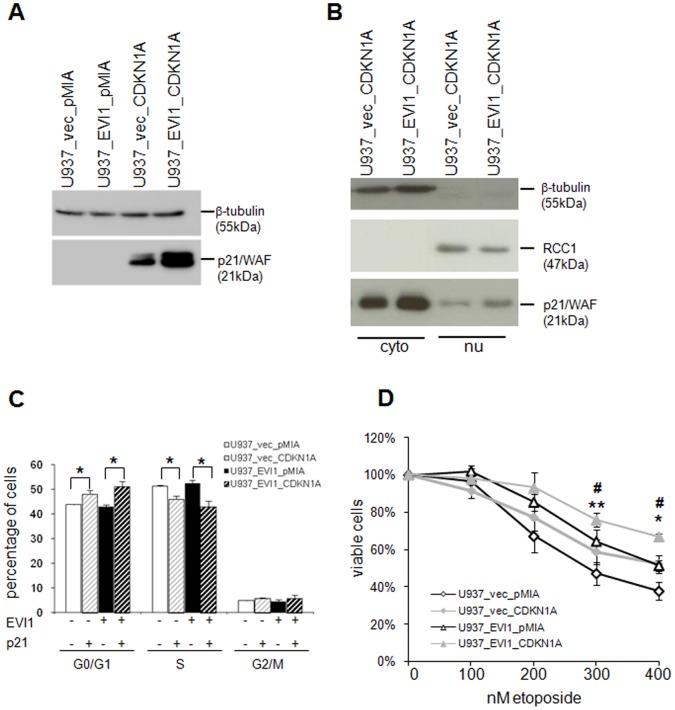
Figure 8. CDKN1A/p21/WAF overexpression partially mimics the chemotherapy resistance phenotype of EVI1 overexpression.
A) Immunoblot analysis confirming overexpressi on of p21 in U937_vec and U937_EVI1 cells infected with pMIA-II_CDKN1A-IRES-Ametrine. β-Tubulin was used as loading control. Detection of endogenous p21 would require longer exposure times. B) Immunoblot analysis of cytoplasmatic (cyto) and nuclear (nu) extracts from U937_vec and U937_EVI1 cells infected with pMIA-II_CDKN1A-IRES-Ametrine. The same amount of protein was loaded in each lane (corresponding to up to twice as many cell equivalents for nuclear versus cytoplasmatic extracts). The cytoplasmatic protein β-tubulin and the nuclear protein RCC1 were used as loading controls. C) Cell cycle distribution of CDKN1A overexpressing and control cells. Shown are means+SEMs from 3 independent experiments. *, p<0.05 (Student’s t-test). D) CDKN1A overexpression increases resistance to etoposide. Cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of etoposide for 48 h and ATP content was determined as a proxy for cellular viability. Shown are means +/− SEMs from three independent experiments. Open symbols, cells without overexpression of CDKN1A; closed symbols, cells overexpressing CDKN1A; diamonds, U937_vec derivatives; triangles, U937_EVI1 derivatives. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01 (paired Student’s t-test; referring to the difference between the U937_vec derived cell lines); #, p≤0.05 (referring to the difference between the U937_EVI1 derived cell lines).