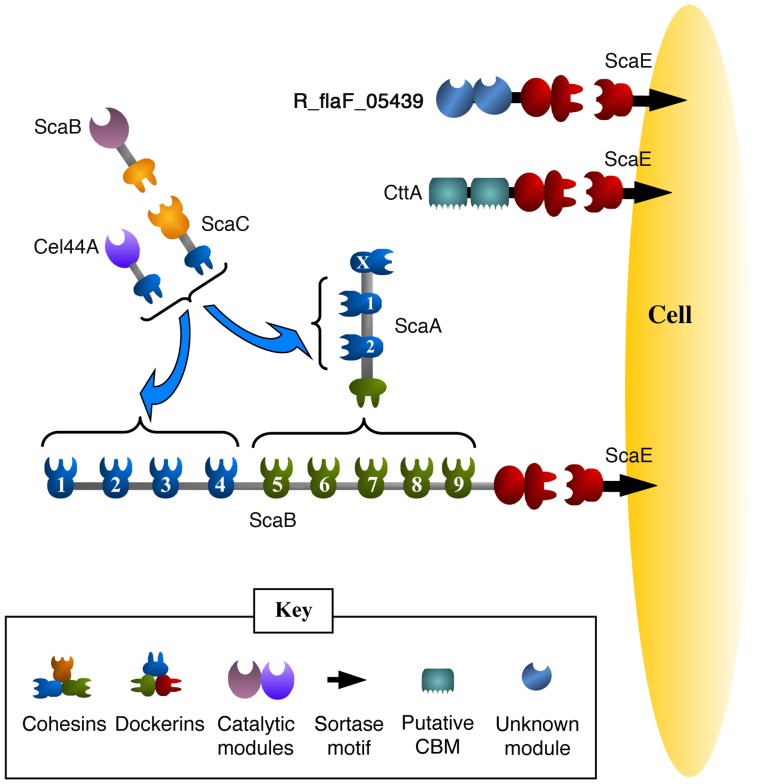
Figure 1. Schematic model of the proposed arrangement of the R. flavefaciens FD-1 cellulosomal components.
The components of the cellulosome include the various scaffoldins (ScaA, ScaB, ScaC and ScaE) and the dockerin-containing catalytic subunits (represented in the figure by the Ce3B-type and Cel44A-type). ScaE is implanted into the cell surface via a sortase-like signal motif. Like the cellulosomal ScaB, two other cellulosome-related proteins, CttA and RflaF_05439, contain an XDoc and are also attached to the cell surface via the ScaE-Coh. The R. flavefaciens FD-1 cellulosome is organized as follows: The ScaA cohesins bind either to the ScaC dockerin or to the various Cel44A-type dockerins, and the lone ScaC cohesin serves as an “adaptor scaffoldin”, which selectively binds to the Ce3B-type dockerins and incorporates their parent proteins into the complex. ScaA is attached via its dockerin into ScaB cohesins 5–9, whereas the specificity of ScaB cohesins 1–4 is similar to those of ScaA.