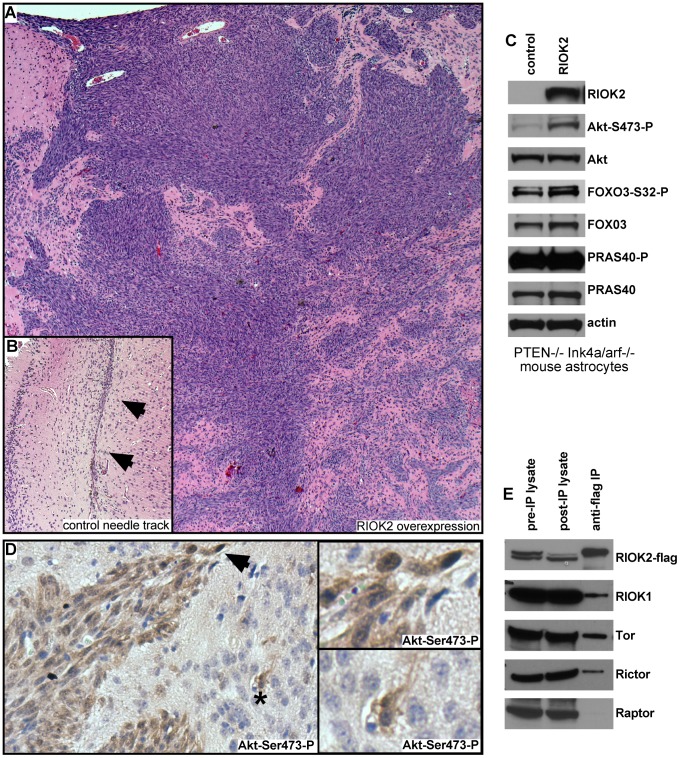
Figure 4. Overexpression of RIOK2 in murine astrocytes promotes tumorigenesis and TORC2-Akt signaling.
(A) H&E stain showing high-grade glioma derived from RIOK2overexpression; Pten−/−; Ink4a/arf−/− astrocytes grafted into the mouse brain. Tumor cells (purple) generate masses composed of spindle-shaped cells as well as infiltrative neoplastic cells that show invasion into the parenchyma and along blood vessels, animals sacrificed ∼19 days following injection. (B) representative needle tract (arrows) in a mouse brain grafted with control Pten−/−; Ink4a/arf−/− astrocytes engineered with empty vector; note the slight concentration of astrocytic cells along the needle tract but no tumor mass or infiltrates. (C) Western blots of RIOK2overexpression; Pten−/−; Ink4a/arf−/− astrocytes compared to Pten−/−; Ink4a/arf−/− astrocytes with empty vector, grown in vitro. (D) Immunoreactivity for Akt phosphorylated at Serine-473 (reddish brown) in a tumor derived from RIOK2overexpression; Pten−/−; Ink4a/arf−/− astrocytes, tumor margin shown, with many surrounding normal cells (purple nuclei, faint staining). Arrow indicates strong staining in invasive cells at tumor margin, asterisk indicates more distant individual invasive cells; both shown in close-up (right). (E) Epitope tagged RIOK2 (RIOK2-flag, runs slightly larger than endogenous untagged RIOK2) was overexpressed in 293T cells and immunoprecipitated along with associated proteins. Blots were probed for indicated proteins, whole lysates from both before (pre-IP) and after (post-IP) are included as a control for protein expression.