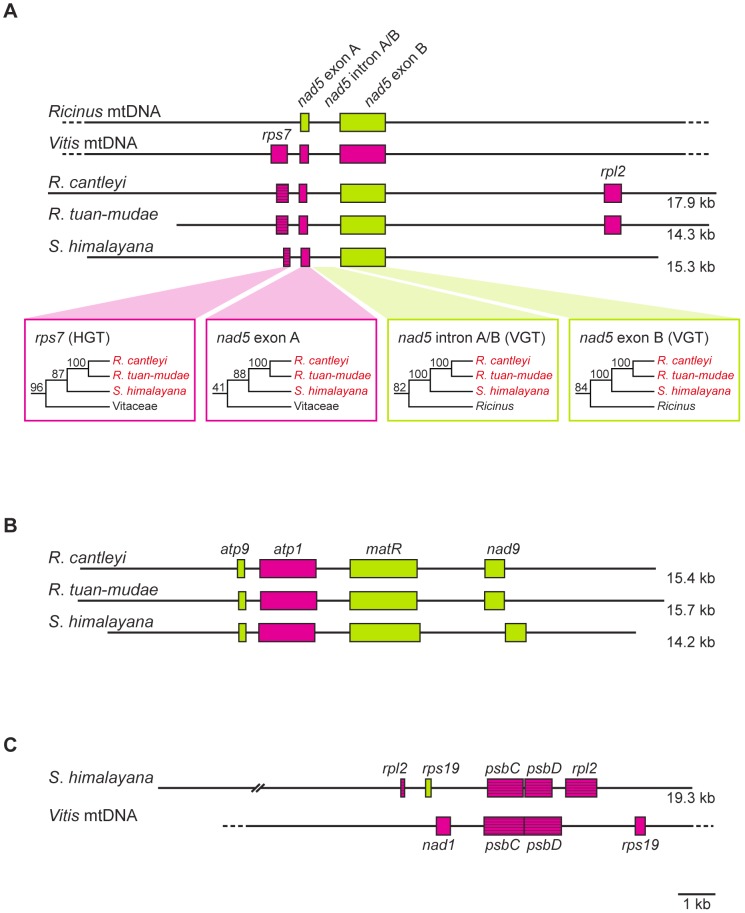
Figure 2. Gene organization of three assembled contigs for Rafflesiaceae (Rafflesia cantleyi, Rafflesia tuan-mudae, and Sapria himalayana), Ricinus communis (Euphorbiaceae), and Vitis vinifera (Vitaceae).
(A–C) The green and red boxes indicate Ricinus-like and Vitis-like genes, respectively. Pseudogenes are represented by striped boxes, and the sequence length (in kilobases [kb]) is indicated to the right of each assembled contig. Gene organization of Ricinus and Vitis mitochondrial genomes (mtDNA) follows Rivarola et al. [20] and Goremykin et al. [23], respectively.