Figure 1. Coronal section of a T1-weighted volumetric MRI from an Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative mild cognitive impairment patient.
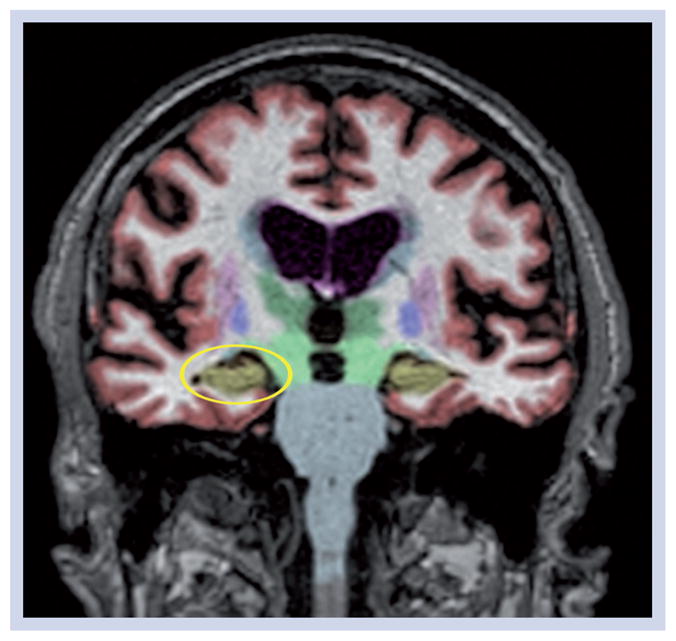
Data have been automatically segmented into different tissue types and brain regions using NeuroQuant® software [101]. The hippocampus, which is highly vulnerable to Alzheimer’s disease, but also affected in other neurodegenerative disorders, is shown in gold. This mild cognitive impairment patient, despite testing positive for cerebrospinal fluid Aβ42 had age-appropriate hippocampal and inferior lateral ventricle volumes (circled in yellow on the left) at baseline and at all follow-ups. This patient retained the mild cognitive impairment diagnosis through 3 years of follow-up.
