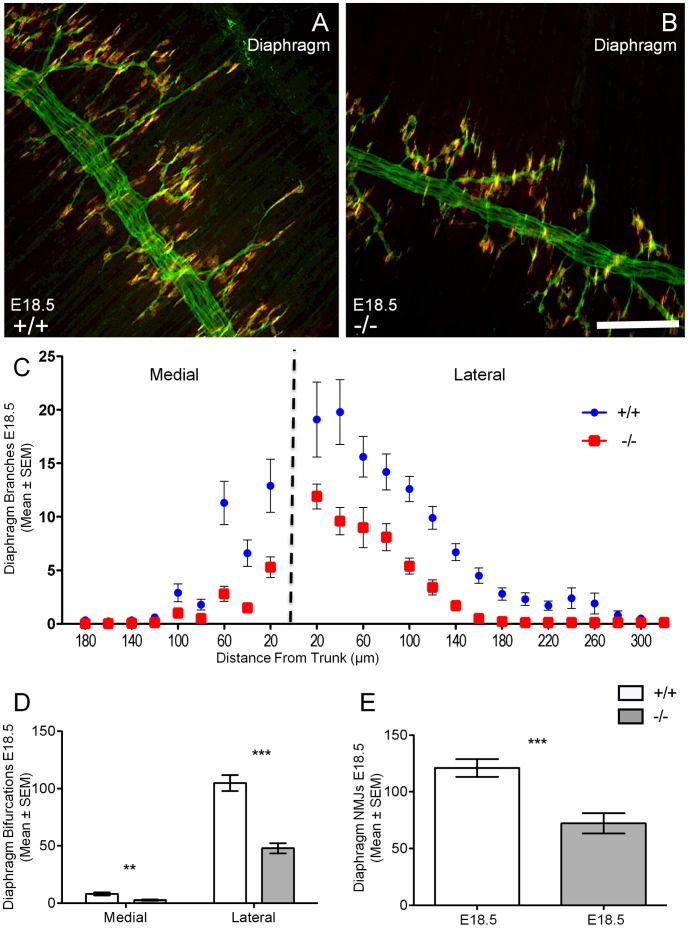
Figure 5. Decreased diaphragm muscle axonal branching distance, bifurcations and neuromuscular junctions in GAD67-deficient (−/−) E18.5 mice.
Axonal branches (green) and acetylcholine receptor clusters (red) in the diaphragm muscle in E18.5 wild type (A, +/+) and GAD67-deficient (B, −/−) are shown. C and D show significant decreases in the number of medial and lateral axonal branches (mean ± SEM) respectively at discrete distances away from main nerve trunk in GAD67-deficient (red) mice compared to wild type controls (blue). D shows a significantly decreased medial and lateral bifurcation number (mean ± SEM) in GAD67-deficient mice compared to wild type (n = 10, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, unpaired t test). E shows a significant decrease in the number of neuromuscular junction endplates in the diaphragm of GAD67-deficient compared to wild type littermates. (n = 10, ***P<0.001, unpaired t test). Scale Bar: A, B, 100 µm.