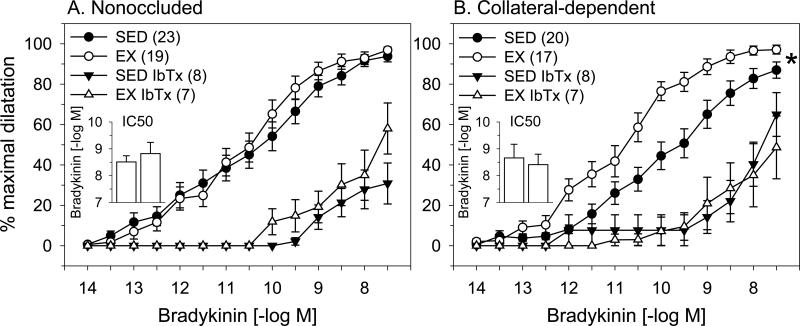
Figure 2. Effect of BKCa channel blockade on bradykinin-mediated dilation of nonoccluded and collateral-dependent arterioles.
The BKCa channel blocker, iberiotoxin (IbTx; 100 nM), significantly attenuated dilation in nonoccluded (A) and collateral-dependent (B) arterioles of sedentary (SED) and exercise trained (EX) pigs. In the presence of iberiotoxin, dilation in nonoccluded arterioles was similar between sedentary and exercise-trained pigs. In contrast, exercise training-enhanced dilation in collateral-dependent arterioles was reverse in the presence of iberiotoxin. In the presence of iberiotoxin, IC50 values were similar in arterioles from the nonoccluded region of sedentary and exercise-trained pigs (2A, inset). Treatment with iberiotoxin reversed the enhanced sensitivity to bradykinin that was observed under control conditions in arterioles from the collateral-dependent region of exercise-trained pigs (2B, inset). Values are means ± S.E.M. of the number of animals in parentheses. * P ≤ 0.05.