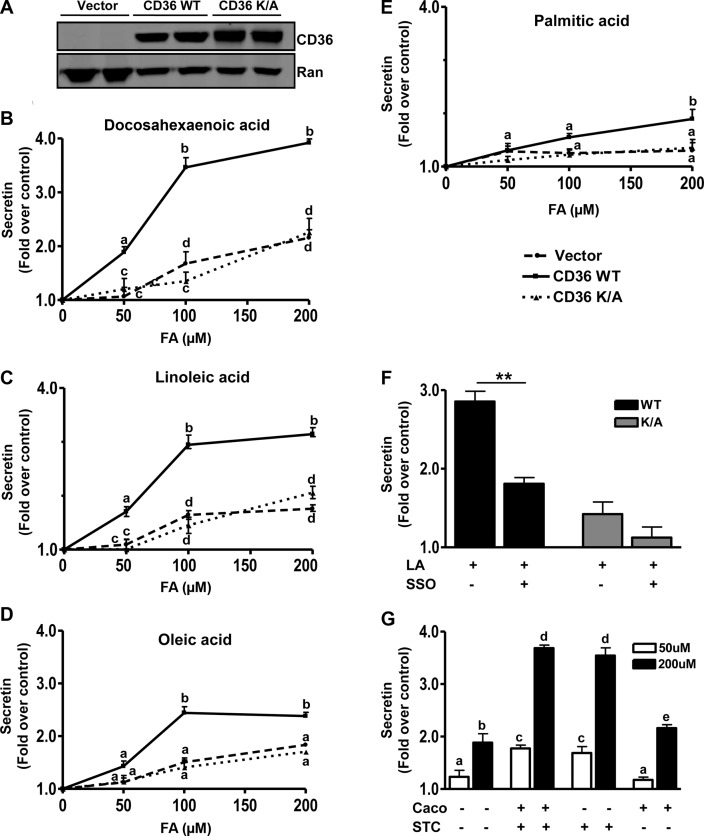
Figure 4.
CD36 enhances FA-induced secretin release from STC-1 cells. A) Western blot showing CD36 expression in STC-1 cells stably expressing empty vector, human CD36 WT, or the CD36K/A mutant. Ran is the loading control. B−E) Secretin release. STC-1 cells were incubated with 50, 100, and 200 μM FA (with 5 μM BSA) or BSA alone (control) in HBSS (no glucose) for 60 min at 37°C, and secretin release was measured after DHA (B), LA (C), OA (D), and PA (E). Release is expressed as fold increase over BSA controls after normalization to cell protein. Data are means ± se of triplicates from 4 experiments (n=12). F) LA-induced secretin release in the presence of the CD36 inhibitor, SSO (20 μM, 15 min). Cells were preincubated with 20 μM SSO for 15 min before stimulation with 100 μM LA. G) Coculture of Caco-2 and STC-1 cells, with or without stable expression of CD36. STC-1 cells expressing CD36 (STC +) or empty vector (STC −) were seeded with Caco-2 cells with (Caco +) or without (Caco −) CD36 expression. Cocultures were serum starved overnight and then were incubated in HBSS with 50 or 200 μM LA (plus 5 μM BSA) or BSA alone (controls) for 60 min at 37°C. Secretin release was determined and is expressed as fold increase over BSA alone after normalization to cell protein. Data are means ± se of triplicates from 3 experiments (n=8–12). Points with different letter symbols are significantly different (P<0.05). **P < 0.01.