Figure 1.
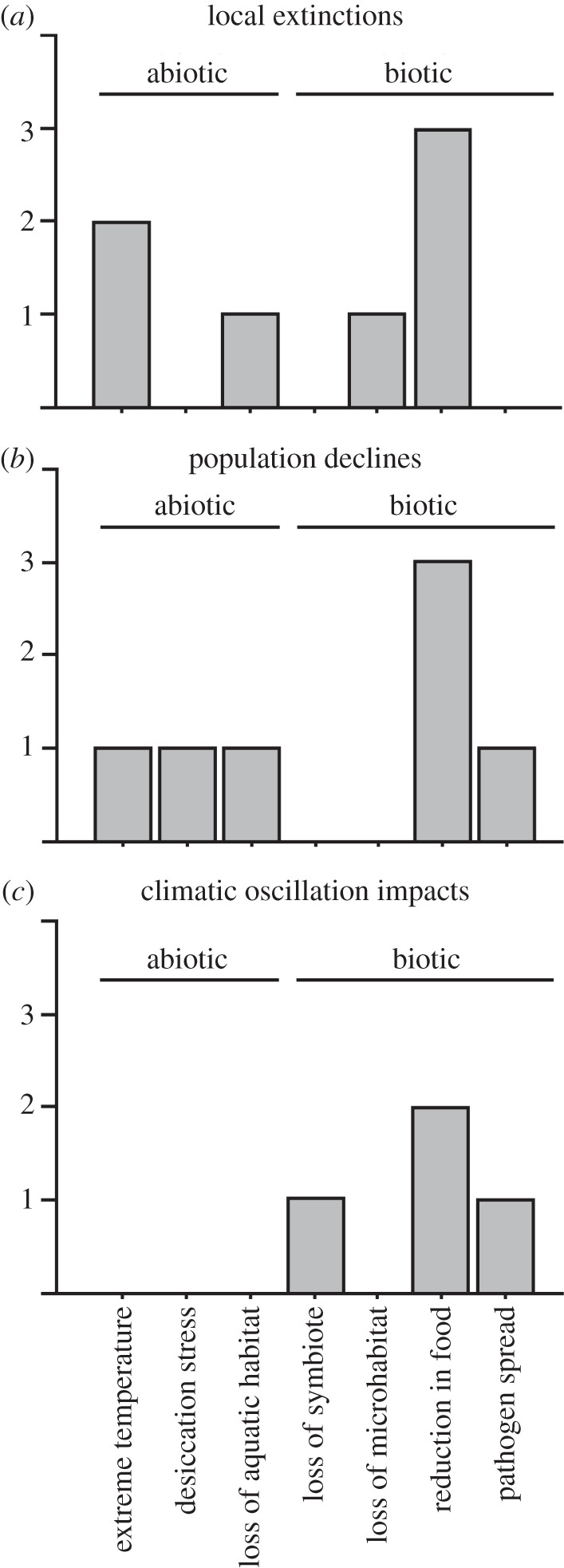
Summary of the frequency of different proximate causes of extinction due to climate change, among published studies. (a) ‘local extinctions’ refers to studies of local extinctions related to anthropogenic climate change (table 1), (b) ‘population declines’ refers to studies of declines in population abundance related to anthropogenic climate change (table 2), whereas (c) ‘climatic oscillation impacts’ refers to studies showing declines related to natural climatic oscillations (table 3) (but these oscillations may also be influenced by human factors, see relevant text). We note that there is some ambiguity in assigning some studies to a single, simple category.
