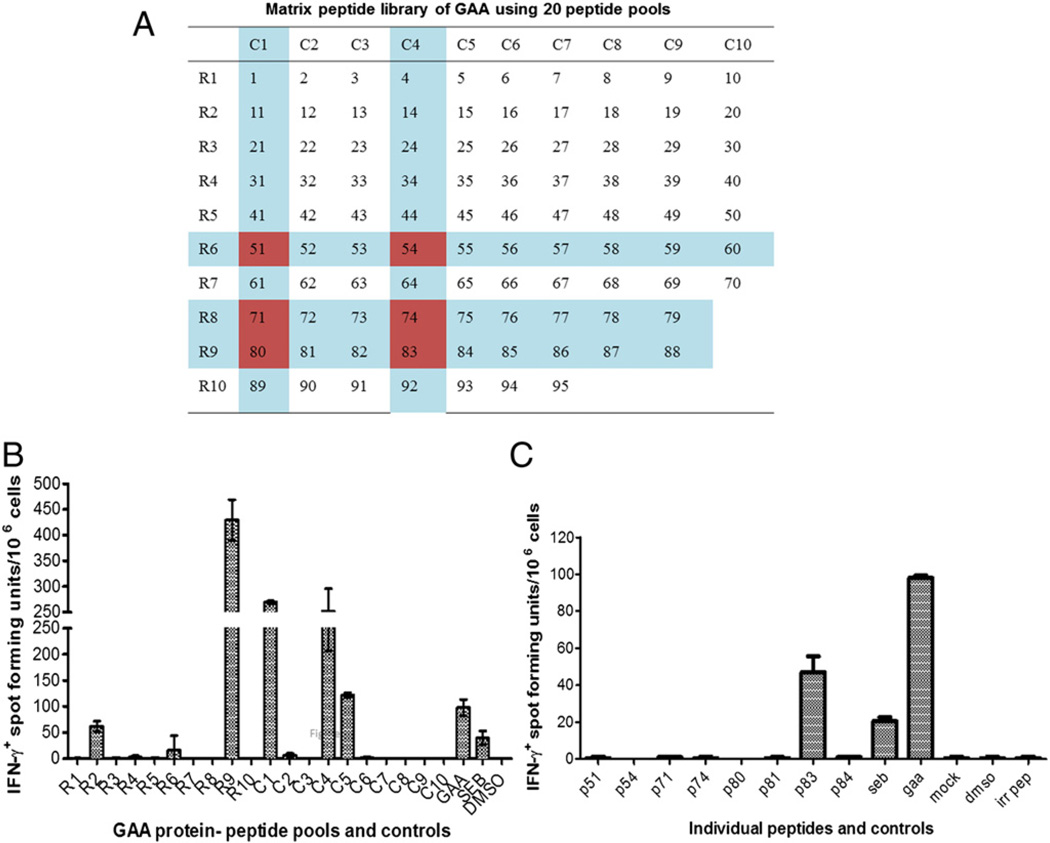
Fig. 2.
Initial identification of a dominant T cell epitope using a peptide library. Pompe mice (GAA−/− 129SVE) were immunized with rhGAA/CFA followed by in vitro stimulation of splenocytes with peptides and IFN-γ ELISpot. A. Matrix of 20 peptide pools, each containing 10 peptides with each peptide being represented in 2 pools. Candidate peptides that emerged from the assay are indicated. B. Average frequencies of IFN-γ spot forming units (± SD) obtained for each pool. C. Average frequencies of IFN-γ spot forming units (± SD) obtained for stimulation with individual candidate peptides. All stimulations were performed in triplicate (using splenocytes pooled from 3 animals). Control stimulations included mock (adding an irrlevant peptide or an identical amount of DMSO solvent to the media), SEB superantigen, and rhGAA protein.