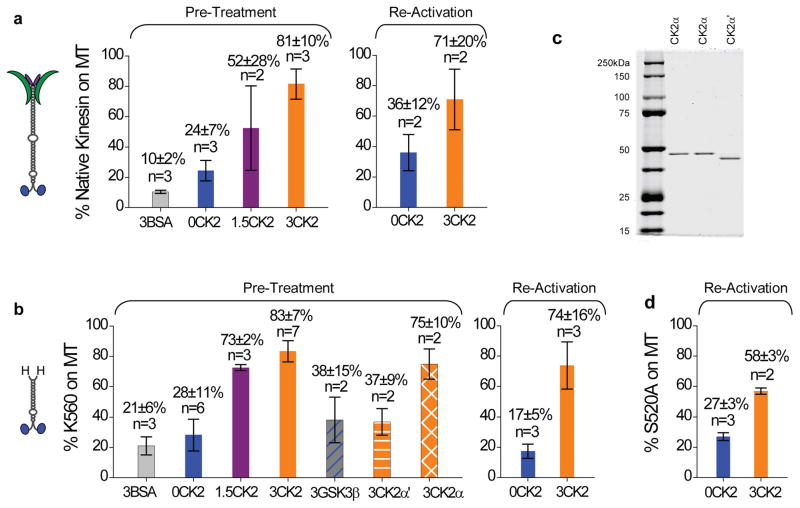
Figure 4.
Quantification of CK2 effect on native and truncated kinesin for both pre-treatment and reactivation. Values are shown in mean±SEM for sample sizes n≥3. For sample size n=2, values are shown in mean±data range. (a) The fraction of native kinesin capable of binding to microtubules vs. input motor amount at 4mM AMPPNP. ‘Pre-treatment’ and ‘Re-activation’ differ in their timing for microtubule pulldowns. For ‘Pre-treatment’ (n = 3–7), kinesin samples were incubated with CK2 or CK2-blank buffer in parallel (1.5 hr on ice), followed by parallel microtubule pulldowns. Three different incubation ratios were tested: 0, 1.5, and 3 CK2 per kinesin (‘0CK2’, ‘1.5CK2’, and ‘3CK2’, respectively). Control experiments replaced CK2 with equal molar amount of BSA (3:1 BSA:kinesin, ‘3BSA’). For ‘Re-activation’, the microtubule pulldowns were staggered in time. We started with kinesin samples that were predominantly inactive (‘0CK2’, n = 3), and evaluated the capacity of subsequent CK2 incubation (1.5 hr on ice) to reactivate these inactive kinesins (‘3CK2’, n = 2). We transferred the inactive kinesin to new plasticware prior to CK2 incubation, thus eliminating the possibility that CK2 functioned by reversing motor precipitation or adsorption to plasticware. (b) The fraction of wild-type tail-less K560 competent to bind to microtubules vs. input (n = 2–6) at 4mM AMPPNP. We employed the same ‘Pre-Treatment’ and ‘Re-Activation’ protocols for K560 as for the native kinesin in (a). In ‘Pre-treatment’, we tested the effect of various proteins in place of CK2, including using BSA (3:1 BSA:K560, ‘3BSA’), a different serine-threonine kinase GSK3β (3:1 kinase:K560, ‘3GSK3β’), and each of the two catalytic subunits of the CK2 holoenzyme (3:1 kinase:motor, ‘3CK2α’ and ‘3CK2α’). (c) Coomassie-stained gels of the two catalytic subunits of CK2: CK2α and CK2α′. Duplicate CK2α lanes are included so as not to disrupt the continuity of the gel. (d) The fraction of phospho-mutant S520A competent to bind to microtubules vs. input (n=3) at 4mM AMPPNP, using the same ‘Re-Activation’ protocol as for the native kinesin (a) and the wild-type K560 (b).