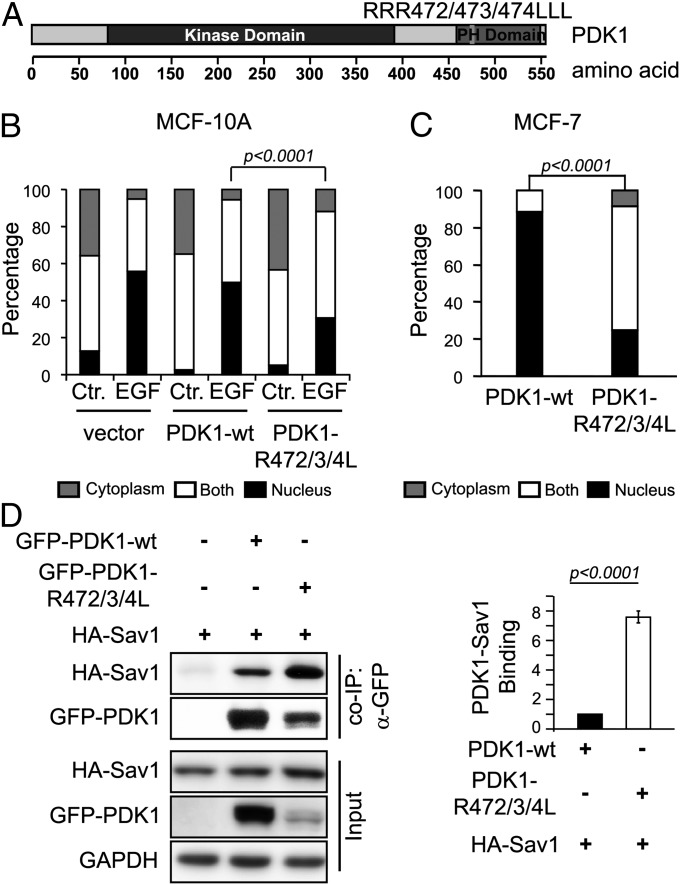
Fig. 6.
PDK1 PH domain is important for EGF-mediated Hippo pathway inactivation. (A) Schema showing overall PDK1 structure and the PDK1 PH domain mutant (RRR472/473/474LLL). (B) PDK1 PH domain defective mutant (PDK1-R472/3/4L) inhibits EGF-stimulated YAP nuclear accumulation in MCF-10A cells. GFP control vector, GFP-PDK1-wt, or GFP-PDK1-R472/3/4L was transfected into MCF-10A cells by electroporation. Serum-starved cells were treated with EGF. The statistical significance of differences in YAP nuclear localization was calculated using the two-sided Fisher exact test. (C) PDK1 PH domain-defective mutant (PDK1-R472/3/4L) causes YAP cytoplasmic retention in MCF-7 cells. GFP-PDK1-wt or GFP-PDK1-R472/3/4L was transfected into MCF-7 cells by electroporation. The statistical significance of differences in YAP nuclear localization was calculated using the two-sided Fisher exact test. (D) PDK1 PH domain-defective mutant binds to Sav1 more abundantly than WT PDK1 in HEK293T cells, determined by co-IP analysis of coexpressed exogenous proteins. Statistical significance was calculated using the Student t test. Error bar represents mean ± SEM; n = 4.