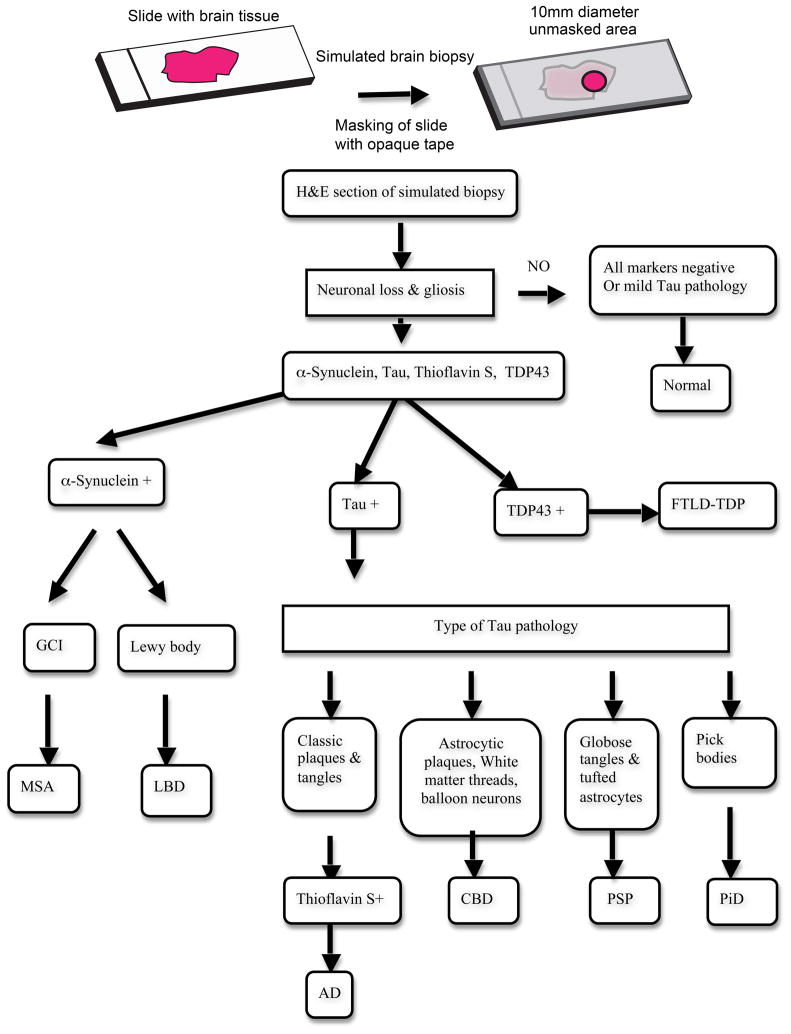
Fig. 1.
Simulated biopsy and diagnostic algorithm. An ideal brain biopsy specimen was simulated on each glass slide in a blinded manner by covering the slide with opaque tape to mask the entire slide except for an area of brain tissue measuring 10 mm in diameter containing a portion of cortex and white matter (except in the case of basal ganglia). The illustrated algorithm was used in the diagnoses of various neurodegenerative disorders in simulated brain biopsies. H&E, phosphorylated tau, α-synuclein, ubiquitin, TDP43 immunostains and thioflavin-S stains were evaluated for each brain region in all cases. Cases positive for α-synuclein were classified as multiple system atrophy (MSA) when glial cell inclusions (GCI) were detected and as Lewy body disease (LBD) when Lewy bodies were identified. Diagnosis of frontotemporal dementia -Tar DNA binding protein 43 (FTLD-TDP) was made when TDP43-positive inclusions were identified. Tau-positive cases were sub-classified based on the presence of characteristic tau-positive features: Pick bodies in Pick’s disease (PiD), white matter threads, astrocytic plaques and balloon cells in carticobasal degeneration (CBD) and globose tangles and tufted astrocytes in progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). Thioflavin-S positive plaques and tau-positive tangles were used in diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease (AD)