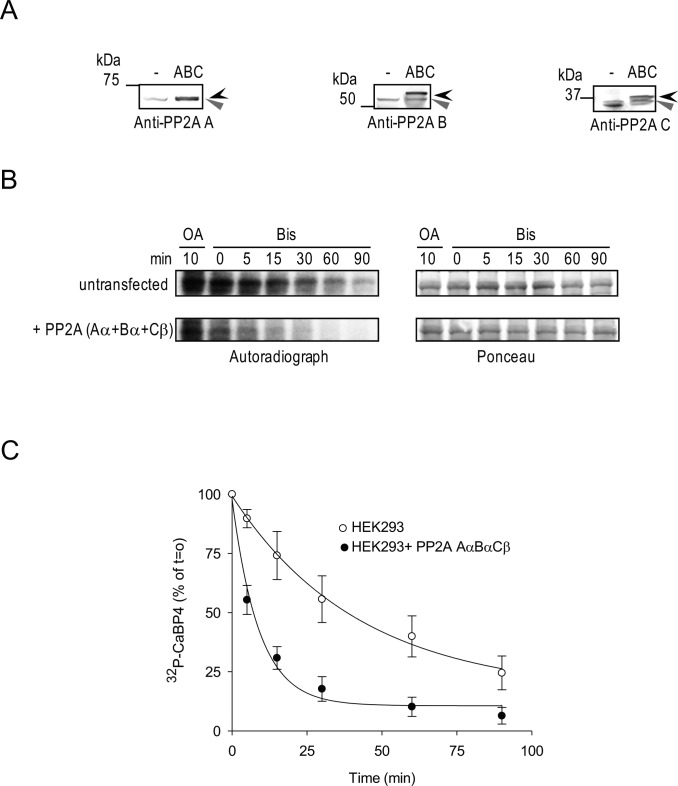
Figure 4. .
Recombinant PP2A subunits enhance CaBP4 dephosphorylation in HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were not transfected (lane 1) or cotransfected with rPP2A Aα, Bα, and Cβ (lane 2). (A) Western blot analysis of the recombinant epitope-tagged (black arrowhead) or endogenous untagged (grey arrowhead) PP2A subunits in HEK293 cell lysates used in (B) using anti-PP2A subunit antibodies. (B) Time course of CaBP4 dephosphorylation by PP2A subunits. Lysates of HEK293 cells were incubated with GST-CaBP4 in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. Similar levels of kinase activity between groups was confirmed upon further incubation with OA (5 μM) for 10 minutes to inhibit PP2A activity. Dephosphorylation of radiolabeled CaBP4 by PP2A was analyzed between 0 and 90 minutes after addition of Bis (10 μM) to inhibit PKC activity. Autoradiograph (left) and Ponceau staining (right) shows levels of phosphorylated CaBP4 and equivalent amounts of CaBP4 in each reaction, respectively. (C) Quantitative analysis of time course of CaBP4 dephosphorylation by PP2A subunits. The intensity of each band of the autoradiography as shown in (B) was quantified using ImageJ and normalized to that of the reaction at T = 0 minutes after quenching of PKC activity. Points represent mean ± SEM, n = 4. The data were fit with a single exponential function. The rate for untransfected cells (1.8 ± 0.7%/min) is significantly slower than that for PP2A-transfected cells (11.8 ± 2.5%/min, P = 0.009 by t-test).