Figure 5.
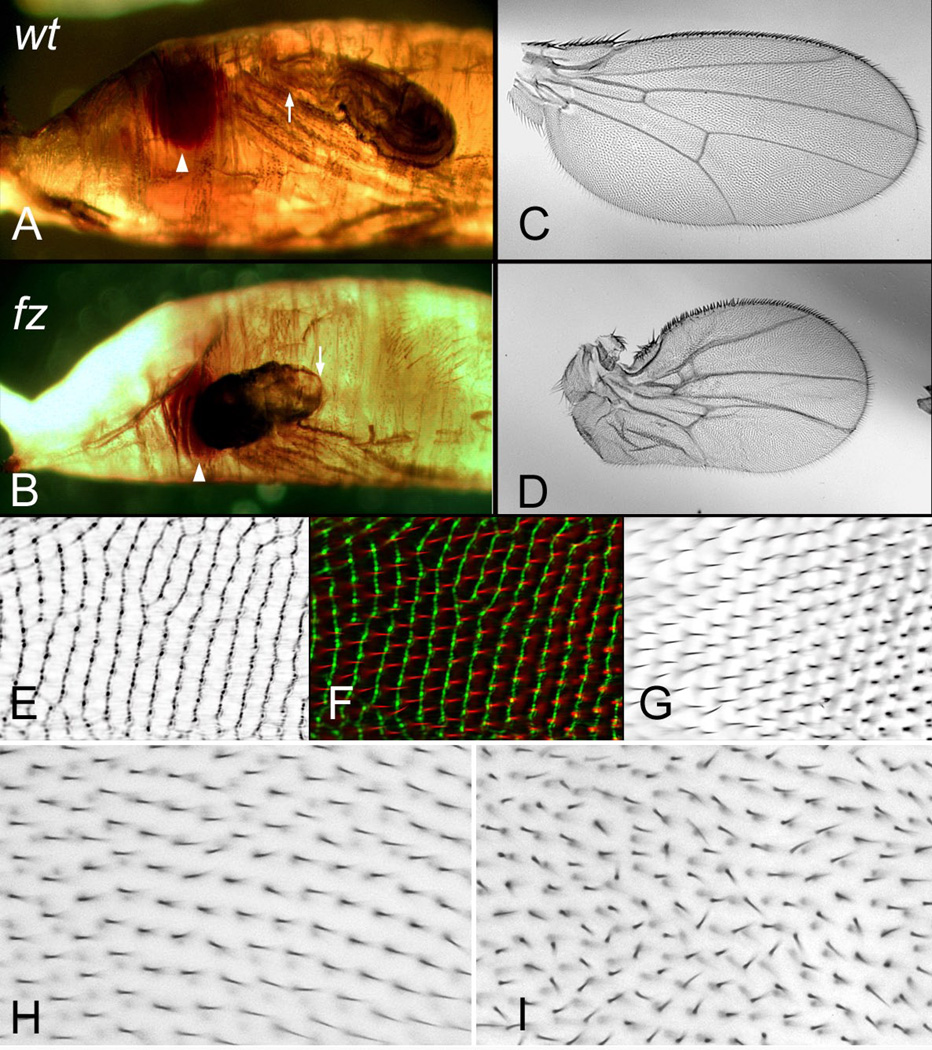
Less well known PCP related phenotypes. Panels A and B show wild type and fz pupae respectively. In a modest fraction of fz pupae the wing everts forward instead of posteriorly (as shown in B). Arrowheads point to the eye and arrows to the wing hinge region. Panel C is a wild type wing and Panel D is a distorted wing that results from the abnormal eversion as shown in B. Panel EFG are wings imaged by Cuticle Reflection microscopy (E) and normal bright field microscopy (G) and a merged image (F). These panels were generously provided by S. Collier. Panel H is a wild type wing and panel I the same region of a wing from a fly homozygous for a mutation in Gliotactin. Note the lack of parallel alignment of neighboring hairs in I.