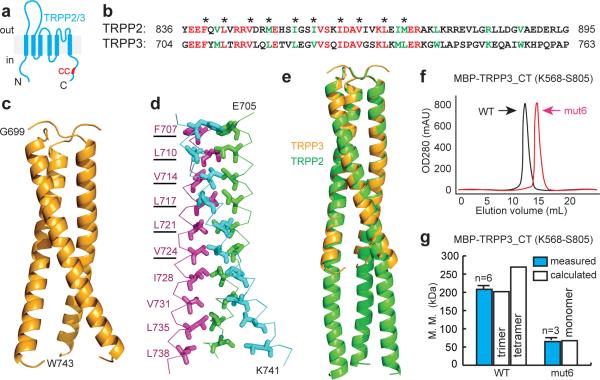
Figure 5. The TRPP3 C-terminus forms a trimer.
(a) Putative transmembrane topology of TRPP2 and TPPP3. The C-terminus of both proteins contains a coiled-coil domain (red bar). (b) Amino acid sequence alignment of TRPP2 and TRPP3 coiled-coil domains. Red: identical; green: conserved. Asterisks indicate hydrophobic residues at the 1st and 4th positions in characteristic heptad repeats of canonical coiled-coil domains. (c) Crystal structure of TRPP3-G699-W743 fragment, showing that the TRPP3 coiled-coil domain forms a trimer. (d) Side-chains, shown in sticks, of hydrophobic residues involved in the formation of the coiled-coil domain trimer. The underlined amino acids were mutated to alanine to generate mut6. (e) Superposition of the structures of TRPP3 and TRPP2 coiled-coil domains (PDB: 3HRN). (f) Gel filtration profile of MBP-tagged WT TRPP3 C-terminal fragment (TRPP3_CT) and TRPP3_CT_mut6. The right shift of the latter indicates a decrease in molecular mass. (g) Bar graph comparing the calculated and measured molecular masses of MBP-TRPP3_CT and MBP-TRPP3_CT_mut6. Measured molecular masses were obtained by static light scattering. Calculated molecular masses were obtained assuming that the protein is a monomer (for mut6), a trimer (for WT), or a tetramer (for WT).
(Yang)