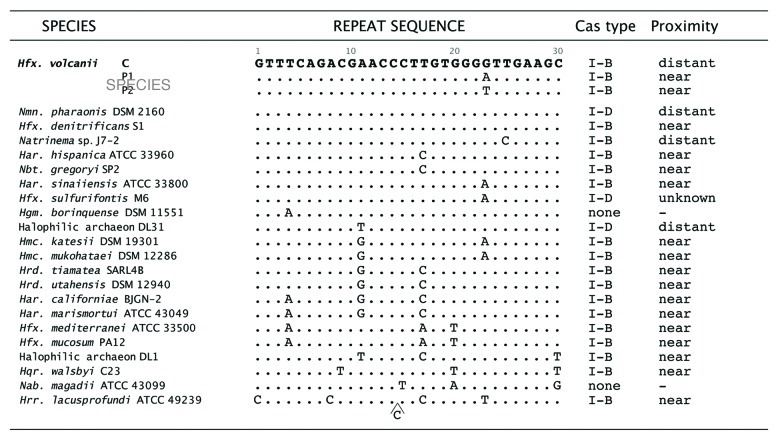
Figure 4. Repeat sequences are conserved in several haloarchaea. The repeat sequence of the Hfx. volcanii chromosomally encoded CRISPR locus C differs from the other two CRISPR loci (P1 and P2) by one nucleotide. The repeat sequence of the chromosomally encoded CRISPR locus (locus C) from Hfx. volcanii was compared (BLASTN) with the haloarchaeal genomes deposited in the NCBI database (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sutils/genom_table.cgi, August 2012) and to the JGI IMG database (http://www.jgi.doe.gov/). In 20 of the 32 additionally available genomes at least one CRISPR locus was found where the repeat was conserved, with only one to five mismatches. All of the repeat sequences shown are part of putative CRISPR loci that contained multiple repeats, and were positively identified as CRISPR loci by the CRISPR finder algorithm at (http://crispr.u-psud.fr/). Whether all of these loci represent intact and functional CRISPR/Cas systems is yet to be determined. a Distant, a cas gene cluster is only found elsewhere in the genome, and is adjacent to another CRISPR locus with a different repeat sequence. b Unknown, the genome sequence remains in numerous contigs, and it is not known if a cas gene cluster is nearby to the CRISPR locus containing this repeat sequence. After the identification of cas gene clusters their proximity to the CRISPR locus was determined by homology searches (e.g., the cas gene finder option at CRISPR finder), followed by manual inspection of the annotated genome sequence. Classification of cas gene clusters was done according to Makarova et al.7cas gene clusters are considered near when they are adjacent to the CRISPR locus and distant if found elsewhere in the genome (where they were usually adjacent to another CRISPR locus with a different repeat sequence). The genome of Hfx. sulfurifontis remains in numerous contigs, so the proximity of cas genes to this locus is currently unknown.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.