Figure 7. Microscopy images of Streptomyces coelicolor pellet compared to model simulations. A.
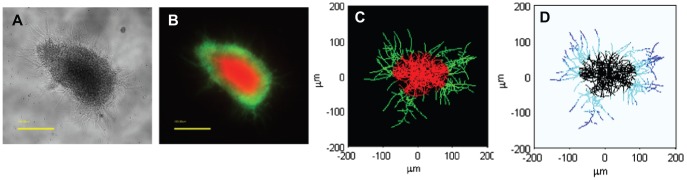
Phase-contrast image of a pellet. B. Fluorescence image of the pellet using green SYTO9 (live cells) and red propidium iodide (likely dead cells) nucleic acid stains. C. Model simulation of a live/dead pellet at the end of the exponentially growing phase. Green colour corresponds to live cells with high consumption rate for oxygen 70% or more, and red colour illustrates the cells surrounded by less than ca 50% of the external oxygen present at the start of the incubation. D. The different metabolic states of the hyphae within the pellet at the end of the exponentially growing phase. Blue colour at the outskirts of the pellet marks the actively growing hyphae. Cyan colour corresponds to hyphae producing antibiotics. Black colour, at the core of the pellet, illustrates metabolically inactive hyphae with only maintenance demands for oxygen.
