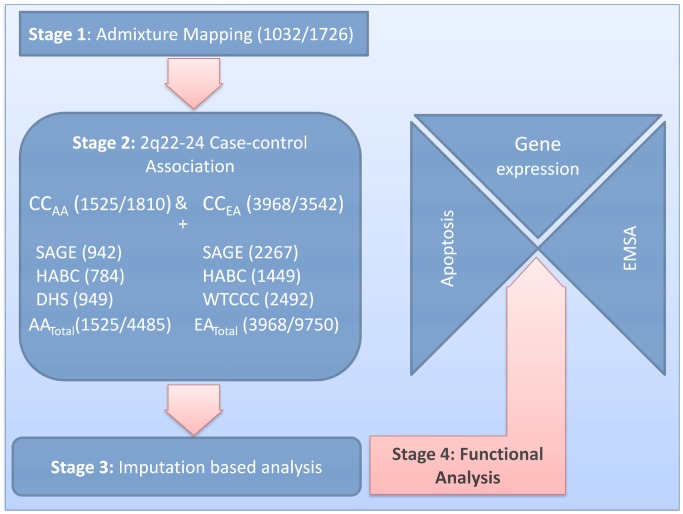
Figure 1. Study design.
Our study design had four stages (sample sizes for cases/controls are in parentheses). In Stage 1, we performed admixture mapping of African Americans (AA) in a case-only analysis with 1032 cases and in a case-control analysis with 1726 controls. In Stage 2, the major admixture mapping signal at 2q22–24 was followed by a candidate gene analysis using case-control association in CCAA (1525/1810) and European Americans (CCEA) (3968/3542), with 737 cases used for stages 1 and 2. In order to focus on our best candidate locus (IFIH1), we used out-of-study controls to increase control sample sizes to 4485 for AA and 9750 for EA. In Stage 3, we performed imputation based analysis on AA (1525/4485) and EA (3968/9750) to confirm our candidate gene analysis. In Stage 4, we performed functional analyses for the three confirmed SNPs. For the coding SNPs rs10930046 and rs1990760, we used an apoptosis assay to assess possible changes in protein function, and a gene expression assay to evaluate the effects of these SNPs on expression of genes related to apoptosis, inflammation and viral response. For the intronic variant rs13023380, we used EMSA to investigate whether the variant affected binding of the local DNA sequence to nuclear proteins.