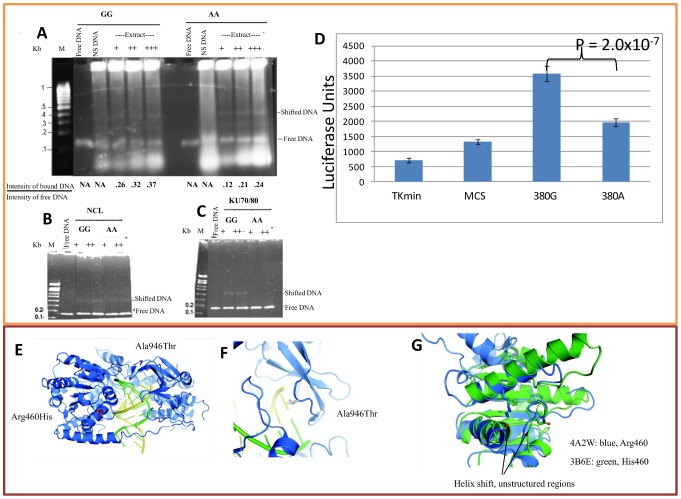
Figure 4. Binding assay for rs13023380 and molecular model of IFIH1.
(A) EMSA was performed using nuclear protein extracts from K562 cells (A) with 141-bp PCR products including either the protective (‘G’) or risk (‘A’) sequence at rs13023380. Both ‘G’ and ‘A’ allele-containing PCR products bound to a protein complex in the nuclear extracts. However, the ‘A’ allele bound with at least 2-fold reduced efficiency compared to the ‘G’ allele-carrying PCR product, as measured by the intensity of the shifted band relative to the free DNA band in the same lane. As a nonspecific (NS) DNA control, a 140-bp DNA sequence not present in the genome was created by PCR amplification of bisulfite-modified genomic DNA. (B, C) EMSA for purified recombinant Nucleolin and Ku70/80 protein with PCR products carrying the ‘G’ or ‘A’ allele of rs13023380. In both the cases, the ‘G’ allele binds both of these proteins with increased efficiency. +signs are used to denote the increasing amount of protein added in the reaction. Numbers below EMSA pictures denote the ratio between the intensities of protein bound DNA to the free DNA. (D) Luciferase activities of intronic DNA sequences carrying ancestral ‘G’ or risk allele ‘A’. The protective allele has approximately 2-fold higher promoter activity (luciferase units) than risk allele ‘A’ carrying sequences. Tkmin-only vector, MCS-vector with multiple cloning sites, 380G-protective allele, 380A-risk allele. (E) Crystal structure of RIG-I in complex with dsRNA (from PDB 3TMI) [27]. Side-chains are shown in red for the positions corresponding to the two coding SNPs in IFIH1. Both mutations are in close proximity to the dsRNA-binding pocket. (F) Close-up of the side-chain of Ala946, modeled from 3TMI. The side-chain makes close contact with the opposing helicase “cap” domain; together these two domains regulate dsRNA entry and processing. Threonine is shown in transparent colors. (G) Superimposition of the RIG-I ATP-binding domain (PDB 4A2W) in blue, and the human IFIH1 ATP-binding domain (PDB 3B6E) in green. The IFIH1 structure contains the histidine side-chain resulting from the rs10930046 risk allele. Large portions of the IFIH1 structure are absent in the 3B6E model, and the two helices are shifted by 1.5 Å. In the ancestral protein, Arg460 likely interacts with the Leu421 main-chain oxygen, as well as the negative helix dipole and the side-chains of Gln433, and Glu425 and 428 (not present in 3B6E).