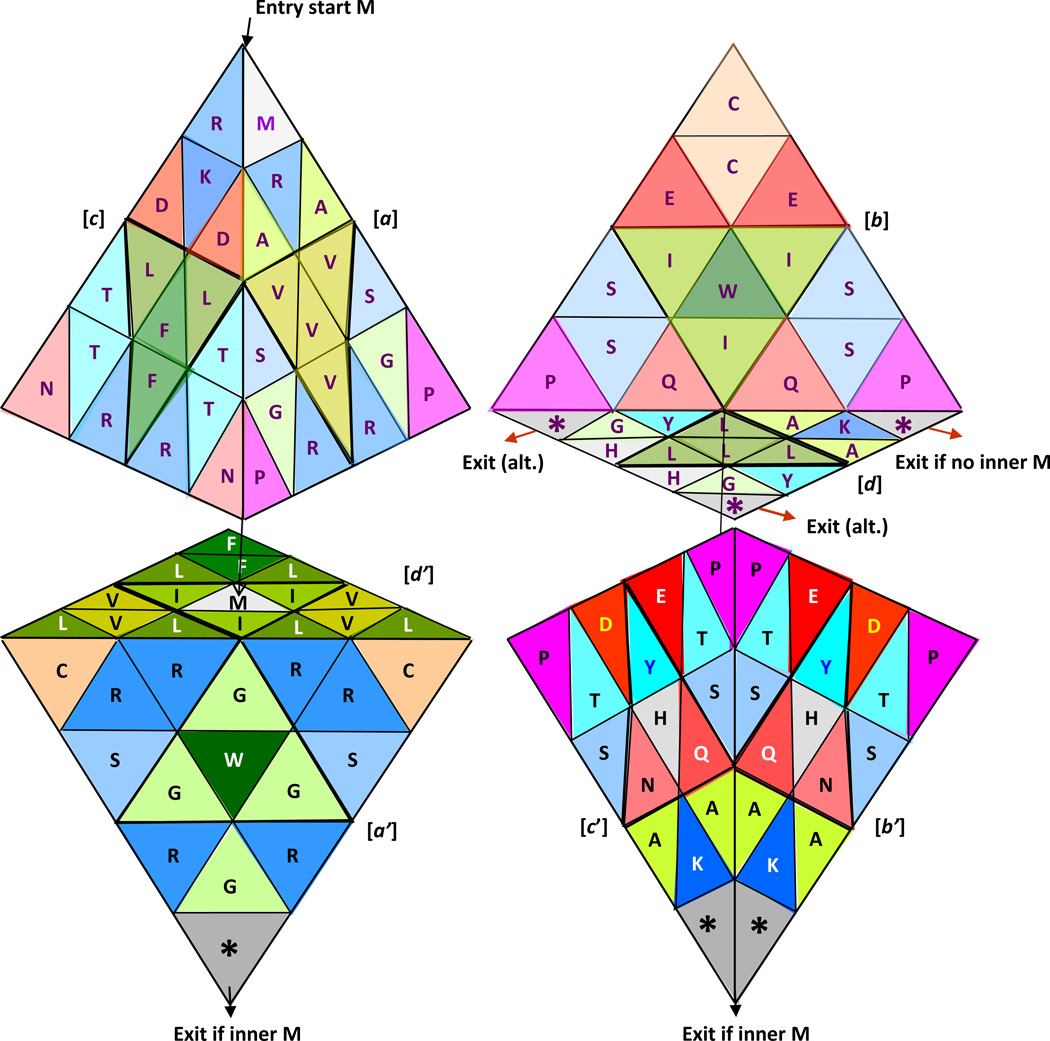
Figure 21.
A 3D diagram of flow for the translation of genes into proteins; two views of the double tetrahedron representing twice the genetic code, as a visual and/or computational strategy to differentiate the start M (ATG) from the non-start M if present, in both a genetic sequence (ATG) or in a peptide/protein; the entry start M (in purple) for the formation of the protein (translation) is indicated by the upper left arrow; if a non-start M is absent, the peptide or protein leaves at one of the three basal apical stop codons from the upper tetrahedron, with the words Exit if no inner M, plus the other two alternative exits: Exit (alt.), shown by the red exit arrows (upper); while on the other hand, if a non-start M is present in a genetic sequence, and in its resulting peptide or protein, as soon as one is detected, the translation moves to the second tetrahedron, being in this case the exit point located at the final apex, at the end, as indicated by Exit if inner M and by the exit black arrows (lower).