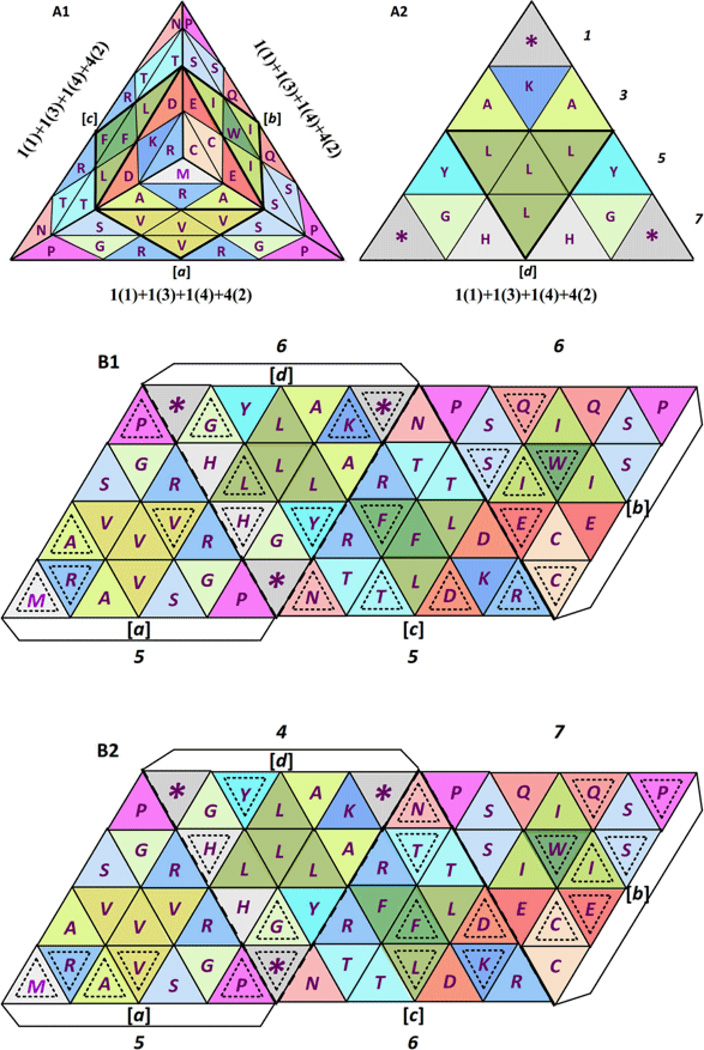
Figure 22.
Codon balance in the standard functional genetic code tetrahedron, seen here from the top (A1) and from the bottom (A2) [1], showing the expanded formula for the balance of codons in the standard functional genetic code tetrahedron: 4[1(1)+1(3)+1(4)+4(2)], where a = b = c = d [1]. Numbers at the right side of A2 show the odd pattern of equilateral triangles per row (1+3+5+7 = 16); comparing in B its alternative 2D parallelogram pattern from which an identical 3D tetrahedron results, like the one shown in A1 and A2, and in the upper half of Figure 21, showing here the position of most used codons per amino acid in man (Homo sapiens): a = c with 5:5 and b = d with 6:6 (B1), compared to the position of most used codons per amino acid in octopus (Octopus vulgaris): d ≠ a ≠ c ≠ b, or 4 ≠ 5 ≠ 6 ≠ 7 (B2).