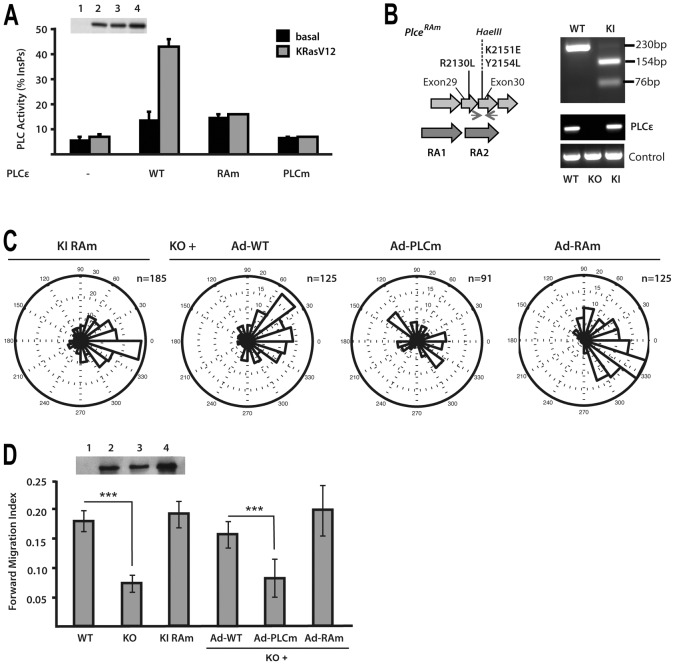
Fig. 4.
Analysis of PLCε functional domains in the context of chemotaxis. (A) Characterisation of PLCε variants with point mutations in the phospholipase C catalytic domain (PLCm) and point mutations in the RA2 domain (RAm). PLC activity of the WT and RAm and PLCm variants was analysed in COS7 cells in the absence (black) or presence (white) of co-transfected KRasV12. Expression level of PLCε WT and PLCm and RAm variants was analysed by western blotting (inset). (B) Strategy to generate PLCε Ras-binding mutant allele (Plce1RAm) by introducing three point mutations (R2130L, K2151E and Y2154L) in exons 29 and 30; the mutagenesis resulted in insertion of a HaeIII site and generated PCR products were analysed by the restriction site digestion. Expression levels were analysed by PCR, using GAPDH as a control. (C) Analysis of immortalised populations of MEFs expressing RAm PLCε variant and KO MEFs infected with Adenovirus expressing the WT (Ad-WT), PLCm (Ad-PLCm) and RAm (Ad-RAm) variants was performed using Dunn chambers. Expression level of PLCε WT and PLCm and RAm variants in PLCε KO cells was analysed by western blotting (inset). (D) Summary of Forward Migration Index values. Data are from four independent experiments using immortalised pools of MEFs; ***P<0.001, ANOVA.