Figure 5.
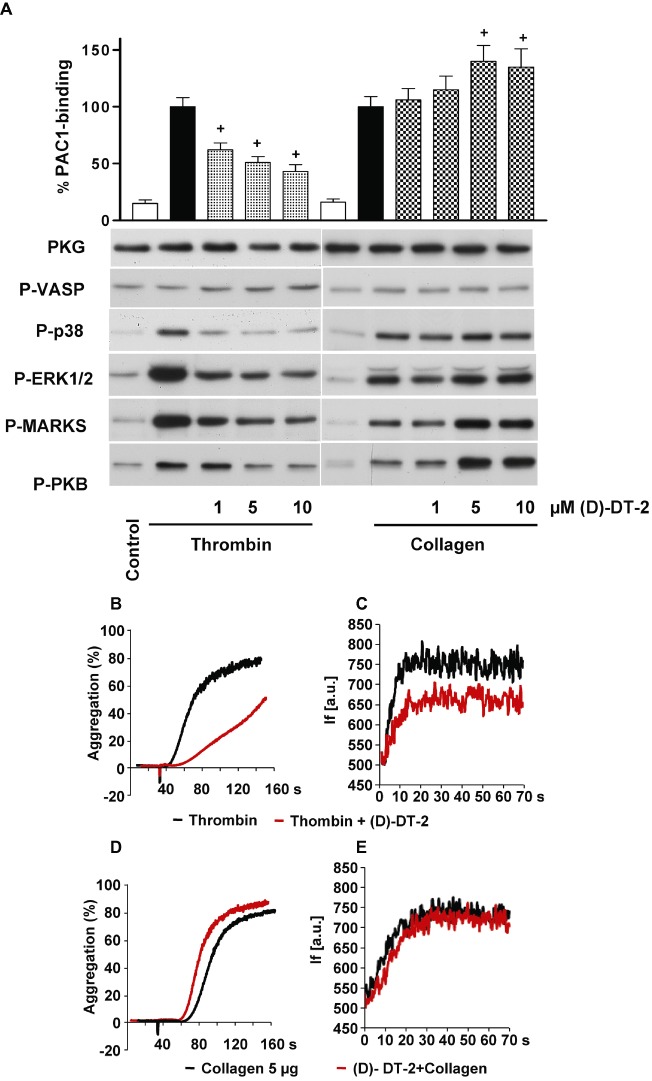
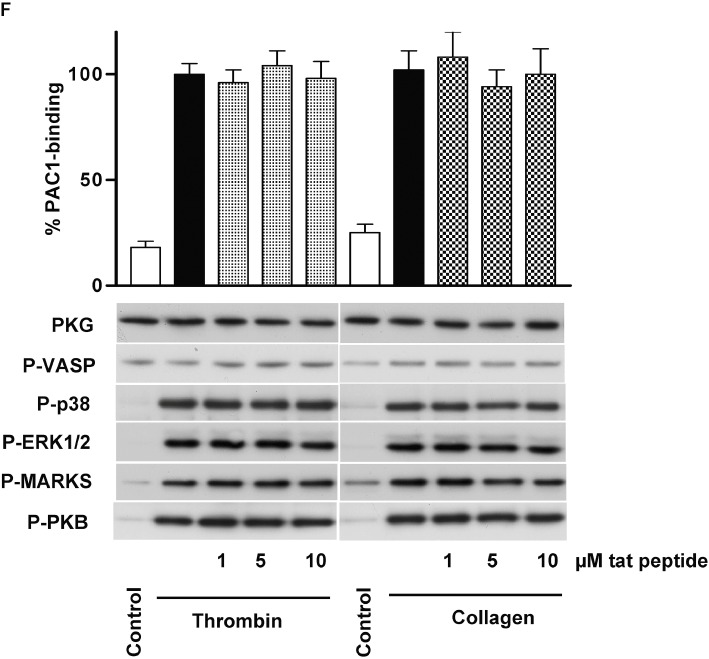
(D)-DT-2 PKG-independently inhibits thrombin-stimulated and enhances collagen-stimulated platelet activation. (A) Human washed platelets were pre-incubated with indicated concentrations of (D)-DT-2 for 10 min and then stimulated with thrombin (0.01 U·mL−1, 1 min) or collagen (5 µg·mL−1, 1 min). 20 µL of platelet suspension was used for FACS analysis of integrin αIIbβ3 activation (PAC-1 binding). The rest of the samples were processed for Western blotting. (D)-DT-2 does not inhibit basal PKG activity in both cases (P-VASP panel); however, it strongly and concentration-dependently inhibits thrombin-stimulated platelet activation assessed by integrin activation (PAC-1 binding). In addition, (D)-DT-2 inhibits MAP kinases (P-p38 and P-ERK1/2 panels), PKC (inhibition of established PKC substrate, P-MARKS panel) and PKB (P-PKB panel). In collagen-stimulated platelets, (D)-DT-2 starting from 5 µM significantly enhances integrin activation which corresponds to increased activation of PKC and PKB. These data correspond to (D)-DT-2 effects on platelet aggregation (B) and calcium mobilization (C) induced by thrombin, or collagen (D, E). Pre-incubation of (D)-DT-2 (10 µM, 10 min) strongly inhibits thrombin-induced platelet aggregation (B) and calcium mobilization (C) and slightly enhances collagen-induced aggregation (D), without affecting calcium mobilization (E). (F) shows the same experiment as in (A) except that (D)-DT-2 was replaced by the tat peptide. All results are representative of at least three independent experiments. Data on PAC-1 binding (A, F) are means ± SEM, n= 4, +P < 0.05 (anova followed by Bonferroni's test).
