Figure 7.
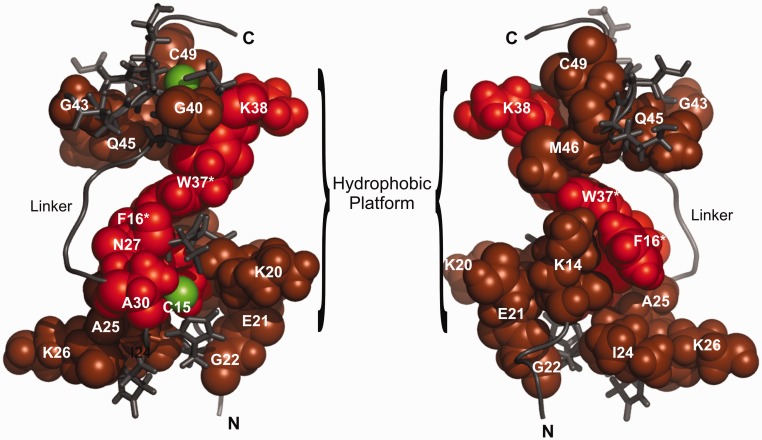
An NMR chemical shift perturbation (CSP) model of NCp7 bound to the DIS kissing complex. The observed CSP of amide resonances of NCp7 are mapped onto the previously determined NMR structure of NCp7 bound to HIV SL2 (PDB id. 1F6U). Residues whose amide resonances showed a significant CSP in both HN and N dimensions are colored red, and the residues with moderate or less CSP are colored in brown. Zinc atoms are shown in green. The N-terminal, C-terminal and Linker regions are denoted by N, C and L, respectively. The terminal residues on both the N and C terminus are not shown, as they were not observed in the HSQC spectrum. More residues in the proximal Zn finger show significant CSP and both the aromatic residues in the fingers F16 and W37 (highlighted with an asterisks) show a significant CSP on binding the RNA kissing complex. Mutating these residues to alanine results in a severe loss of chaperoning activity of the protein. Interestingly, alanine at position 30, presumed to be at a distant site from the RNA-binding interface, also shows significant CSP on binding the kissing complex, suggesting a conformational change in the linker structure that might reorient the two Zn fingers to accommodate proper stacking interactions between the kissing helix residues of the RNA and the aromatic acid residues of the protein. The hydrophobic patch that facilitates binding of RNA is also indicated.