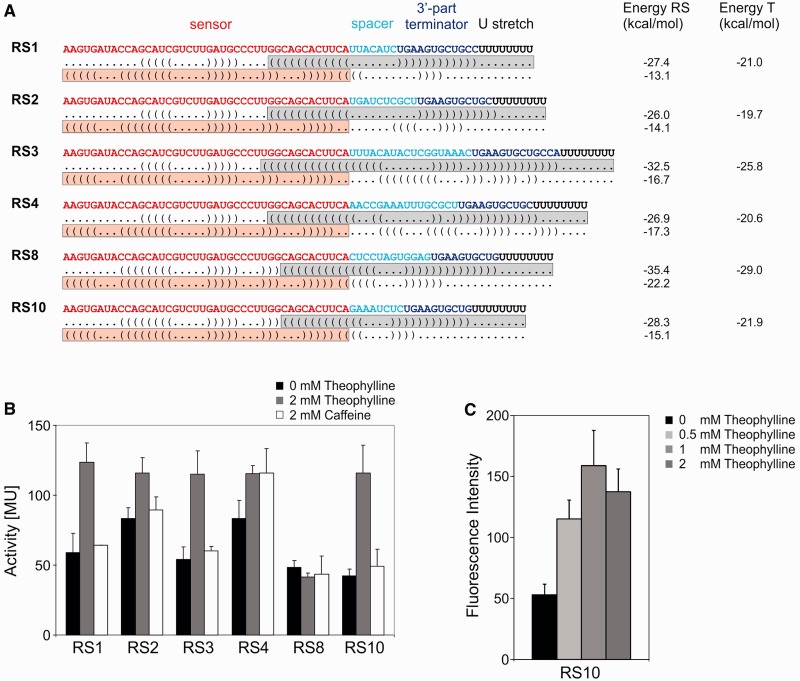
Figure 2.
Riboswitch constructs and activity tests. (A) The theophylline aptamer represents the sensor (red), followed by a variable spacer sequence (cyan) and the 3′-part of the terminator (blue), forming a hairpin structure with a subsequence of the sensor domain. The terminator element is completed by a stretch of eight U residues (black). Below each construct, dot bracket notations of the secondary structures with terminator or antiterminator formation are indicated. The overlapping situation of sensor (theophylline aptamer, red box) and actuator element (terminator element, grey box) is required for a mutual exclusion of the two alternative structures. For each construct, calculated energy values of complete riboswitch elements (RS) and isolated terminators (T) are indicated. (B) Activity tests of the reporter enzyme β-galactosidase. Activities are indicated in Miller units (MU). All synthetic riboswitches were tested in the absence (black bars) and presence (gray bars) of 2 mM theophylline. As a control, the structurally related caffeine was offered (white bars). (C) Activity test of RS10 under the control of the Prrn promoter and GFP as reporter gene. Relative fluorescence signals are indicated as a function of theophylline concentration. The riboswitch shows a similar regulation profile as in (B), indicating the general functionality of the construct.