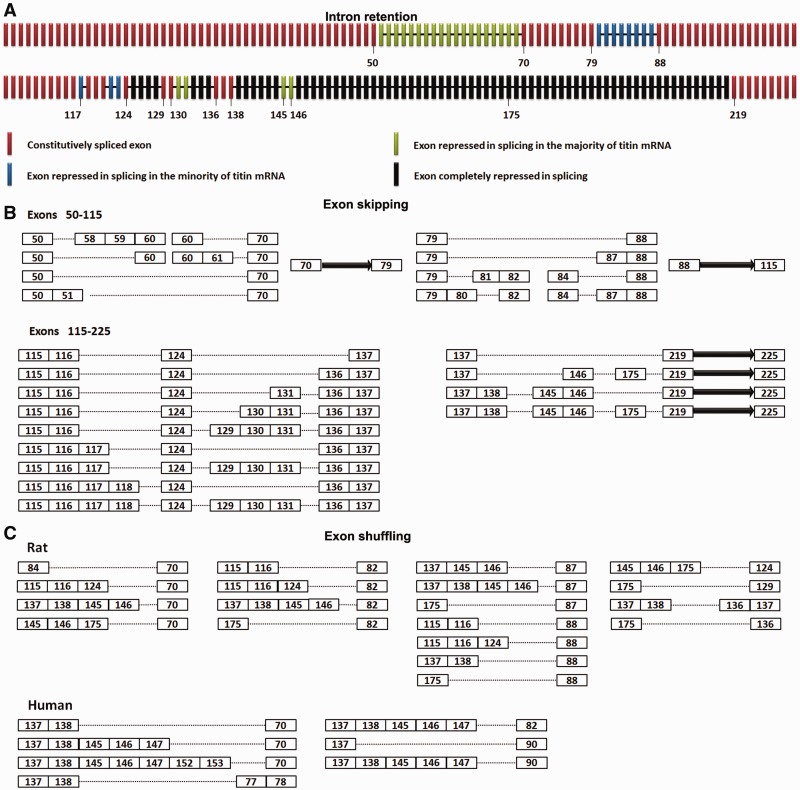
Figure 2.
Rbm20 mediates exon skipping and exon shuffling. (A) Schematic illustration of intron retention along cardiac titin mRNA in Wt rats. The titin exons and retained introns are shown with bars and lines, respectively. Colors denote the extent of Rbm20 repression on different regions. Black: complete repression, splicing repressed in all mRNAs; green: strong repression, splicing repressed in the majority of mRNAs; blue: mild repression, splicing repressed in the minority of mRNAs; red, no repression, normally spliced. The numbers of some exons are indicated. (B) Schematic illustration of exon skipping along cardiac titin mRNA in the Wt rat. The exons are displayed as numbered boxes; the solid arrow represents consecutive exons that result from constitutive splicing between the adjacent numbered exons. The dotted lines denote the exon skipping mediated by direct ligation between adjacent numbered exons. Results show that exon skipping only occurs in the Rbm20-repressed regions: exons 50–70, exons 79–88 and most of the PEVK region.(C) Diagram depicts the exon composition of exon-shuffling isoforms from the cardiac titin mRNA in the Wt rat and human. The exons are shown in numbered boxes, and the dotted lines denote direct attachment between the adjacent numbered exons.