Figure 1.
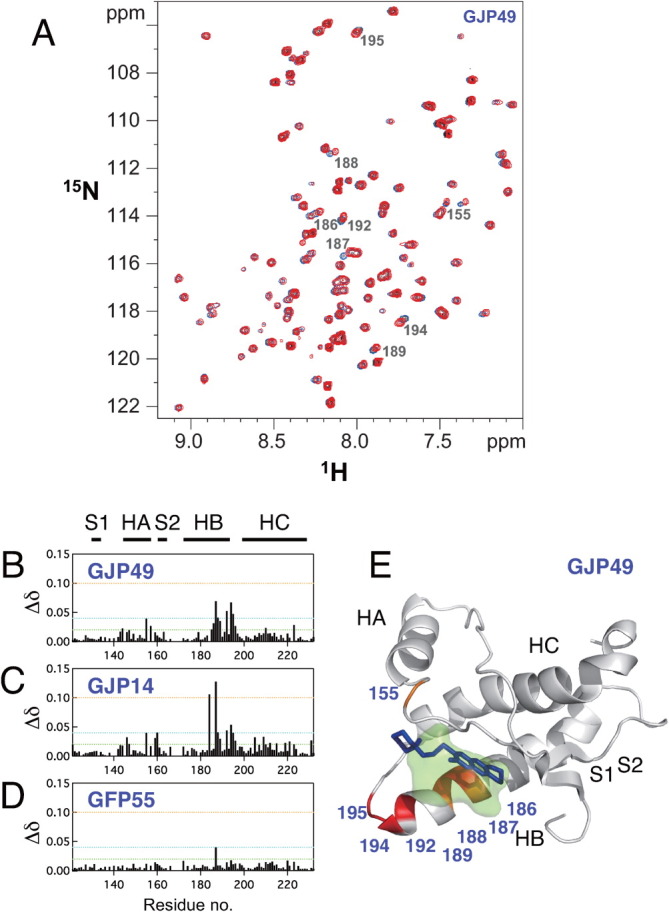
Characteristics of the binding sites for the antiprion compound GJP49. GJP49 was discovered by in silico screening using Autodock.7 (A) 1H-15N HSQC spectra of 15N-labeled recombinant prion protein, mouse PrP(121–231) (33 μM), with (red) or without (blue) GJP49 (500 μM). (B–D) Plots of chemical shift perturbations (Δδ = [(Δδ1H)2 + 0.17(Δδ15N)2]1/2) as a function of the residue number. (E) Mapping of the significantly perturbed residues on the three-dimensional structure of the prion (1AG2). The perturbed residues with Δδ values of >0.04 ppm are shown in red, and those with 0.4 < Δδ < 0.3 ppm are shown in orange. The binding pocket is overlaid in green. S1, HA, S2, HB, and HC indicate S1 strand, helix A, S2 strand, helix B, and helix C, respectively. The image was created using PyMol.
