Figure 1.
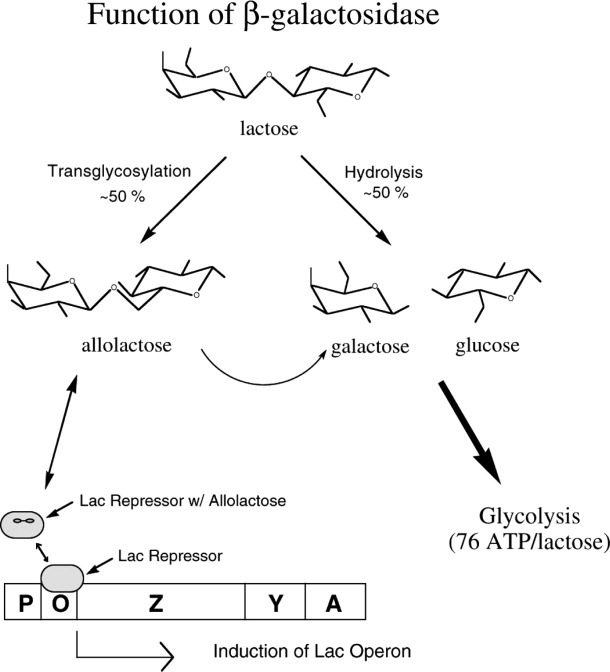
Schematic summarizing the roles of β-galactosidase in the cell. The enzyme can hydrolyze lactose to galactose plus glucose, it can transgalactosylate to form allolactose, and it can hydrolyze allolactose. The presence of lactose results in the synthesis of allolactose which binds to the lac repressor and reduces its affinity for the lac operon. This in turn allows the synthesis of β-galactosidase, the product of the lacZ gene.
