Fig. 1.
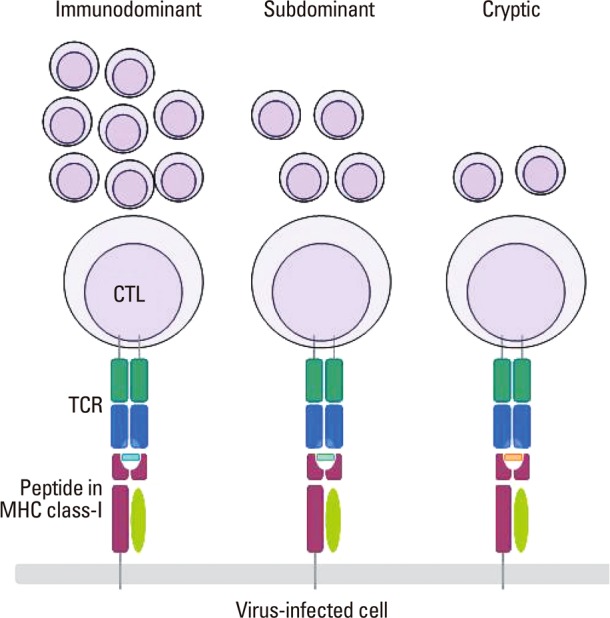
T cell Immunodominance. Virus-specific CTLs recognize the complex of the viral peptide and MHC class-I molecule presented on the membrane of the infected cells. Some peptides generate strong signals and thereby lead to the robust clonal expansion of the responding CTLs (immunodominant), some generate weak (subdominant) signals, and others barely generate a signal (cryptic) only detectable in the absence of the others. The hierarchy of the T cell immunodominance shaped by primary exposure to a virus varies upon a subsequent infection with heterologous virus. CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; TCR, T cell receptor; MHC, major histocompatiblity complex.
