Fig. 4.
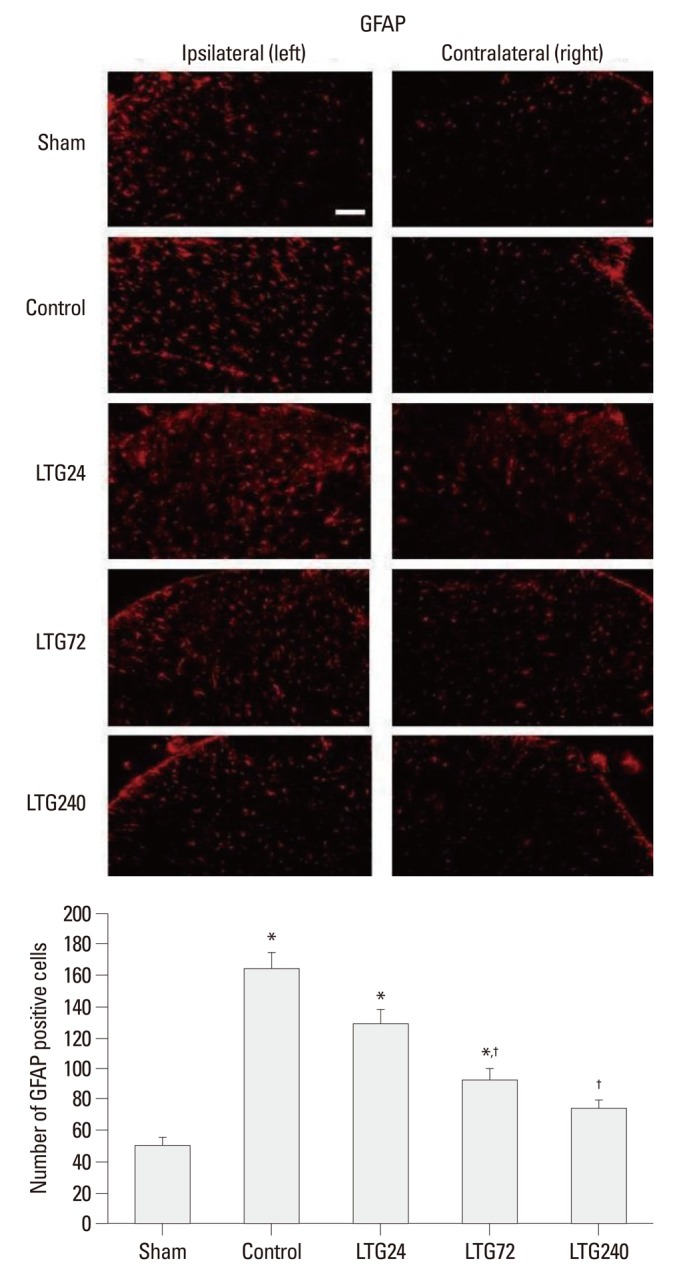
Effect of lamotrigine on spinal immunoreactivity to GFAP after left L5/6 spinal-nerve ligation. Rats were continuously administered 24, 72, and 240 µg per day lamotrigine or intrathecal saline for 7 days after spinal nerve ligation. Prominent astrocytic activation was observed in the ipsilateral side spinal cord of rats in the control group. No group showed significant changes in the contralateral side spinal cord. Nerve ligation-induced astrocytic activation was markedly suppressed by 72 and 240 µg intrathecal lamotrigine. Scale bar: 100 µm. *p<0.05 compared with the sham group, †p<0.05 compared with the control group, by one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's test (n=6 per group). GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein.
