Figure 2. PrPC Vesicles Associate with Kinesin-1 and Dynein.
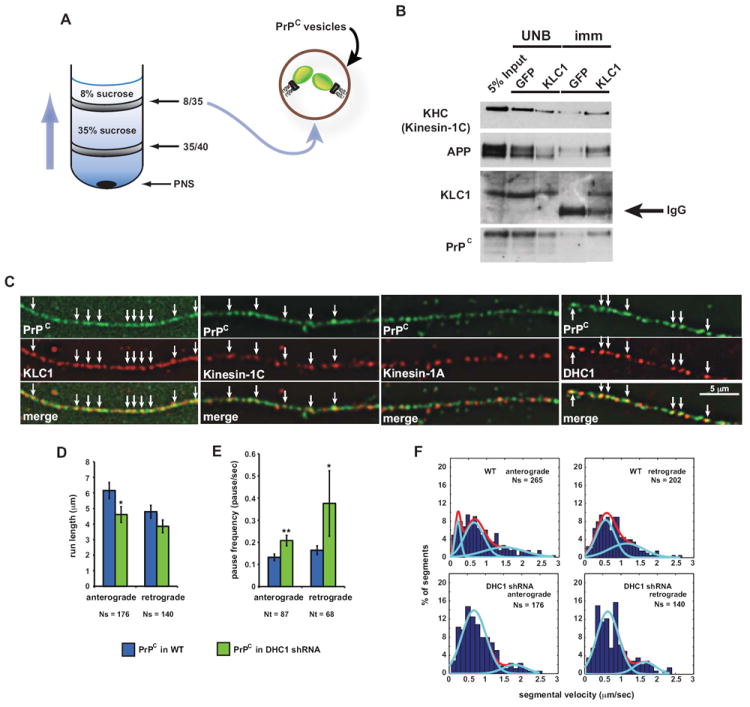
(A) Schematic diagram of a membrane flotation experiment showing the 8/35 fraction used as starting material for the vesicle immunoisolation in (B). Wild-type post-nuclear supernatant (PNS) obtained from wild-type mouse brain homogenate was bottom loaded. Buffers used did not contain detergent to prevent breaking of membranes.
(B) An antibody against KLC1 was used to pull down associated membrane components from 8/35 fractions, including PrPC-containing vesicles. KHC antibody recognizes mostly Kinesin-1C. UNB = unbound fraction; imm = immunoisolation. Anti-GFP was used as a control.
(C) Deconvolved images of vesicles stained with antibodies against PrPC and KLC1, Kinesin-1C, Kinesin-1A, or DHC1. Arrows point to some colocalization events.
(D) Run length and (E) pause frequency in DHC1 shRNA axons. All values are shown as mean ± SEM. **p<0.01, *p<0.05, permutation t-test.
(F) Segmental velocity histograms (shown as percent of segments) of YFP-PrPC transport in wild-type and DHC1 shRNA axons. Red and light blue curves represent the overall and predicted Gaussian modes, respectively.
Ns = # segments; Nt = # tracks. See also Figure S2.
