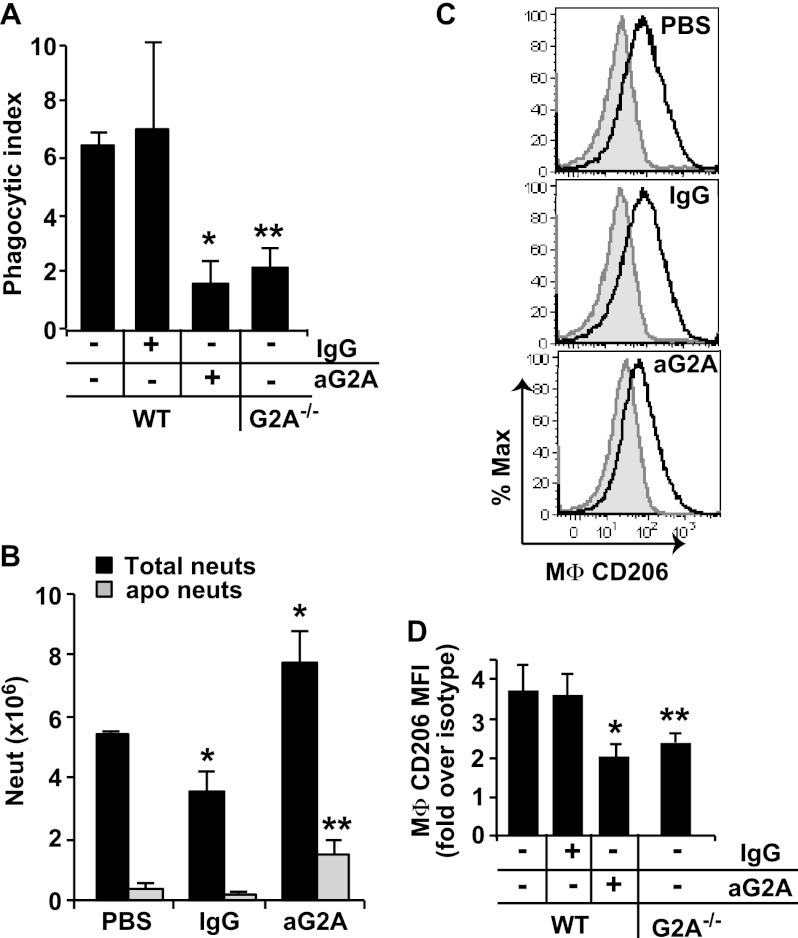
FIGURE 5.
Endogenous lyso-PS signaling via G2A promotes the development of CD206high efferocytic macrophages and resolution of neutrophilia. WT mice were injected intraperitoneally with 100 μg of blocking antibody to G2A (or IgG isotype control or PBS) at 18 h after induction of zymosan peritonitis. Thirty hours later, peritoneal cells were collected by lavage and analyzed. For comparison, cells from G2A−/− mice at 48 h into zymosan-induced peritonitis were also analyzed. A, phagocytic indices were determined by visual inspection of cytospins. n = 6–8; *, p < 0.05 compared with WT control in the absence of antibody blockade; **, p < 0.05 compared with WT control. B, total neutrophils (neuts) and total apoptotic neutrophils (as determined by morphology from cytospins) were quantified. n = 5; *, p = 0.03 compared with WT PBS control; **, p < 0.02 compared with WT PBS control. C, CD206 expression on F4/80+/Ly6G− MΦ was determined by staining with anti-CD206 (solid line) or CD206 isotype control antibody (shaded gray) and analyzed by flow cytometry (shown are representative histograms from six independent experiments). D, geometric means of CD206 expression was determined and expressed as fold over CD206 isotype control staining and summated for WT and G2A−/− peritoneal MΦ. n = 6; *, p < 0.02 compared with WT control; **, p = 0.01 compared with WT control. Data represent mean ± S.E.