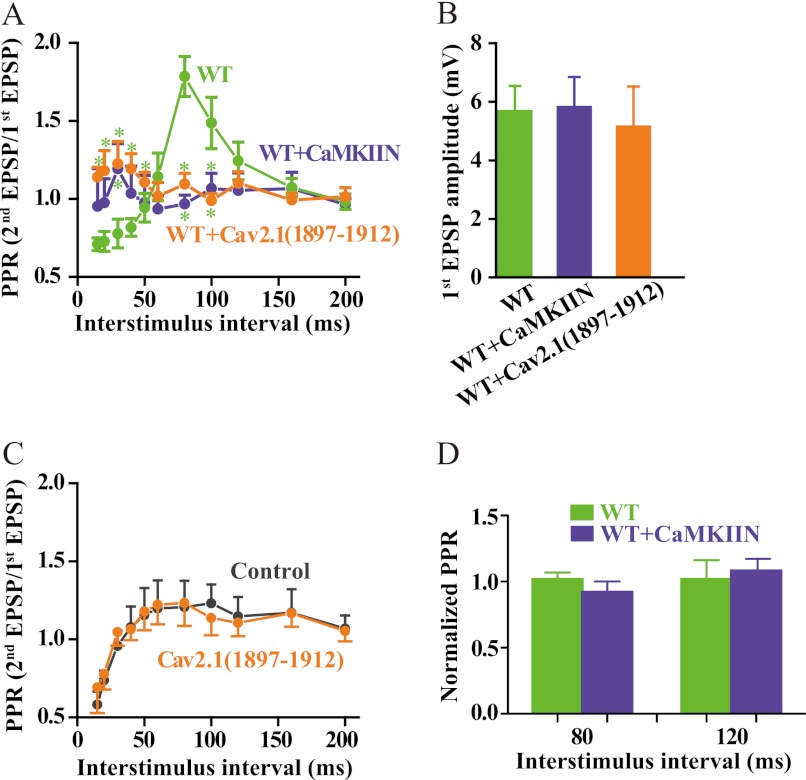
FIGURE 10.
Binding of CaMKII to CaV2.1 channels is required for short term synaptic plasticity. A, SCG neurons were cultured and injected with cDNA encoding CaV2.1 channels as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Where indicated, CaMKIIN was co-expressed with CaV2.1 channels, or CaV2.1(1897–1912) was injected through a whole-cell patch electrode 30 min before recording as described (39). Sharp microelectrode impalements were made in the previously transfected, presynaptic neuron and a neighboring, synaptically connected neuron. Action potentials were generated in the presynaptic cell, and EPSPs were recorded in the postsynaptic cell and analyzed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The paired-pulse ratio (PPR) was plotted against inter-stimulus interval (mean ± S.E.; *, < 0.05, Student's t test, n = 6–9). WT, green; CaMKIIN, blue; CaV2.1(1897–1912), orange. B, amplitudes of the first EPSP in paired pulse experiments are shown. C, a similar experiment to that described in panel A was carried out with CaV2.1(1897–1912) injected through a whole-cell patch electrode in untransfected SCG neurons, and paired-pulse facilitation of neurotransmission initiated by the endogenous CaV2.2 channels was measured in the absence of ω-conotoxin GVIA. D, a similar experiment to that described in panel A was carried out with expression of CaMKIIN in untransfected SCG neurons, and paired-pulse facilitation of neurotransmission initiated by the endogenous CaV2.2 channels was measured in the absence of ω-conotoxin GVIA. Normalized paired-pulse ratios of control and CaMKIIN-expressing neurons are plotted.