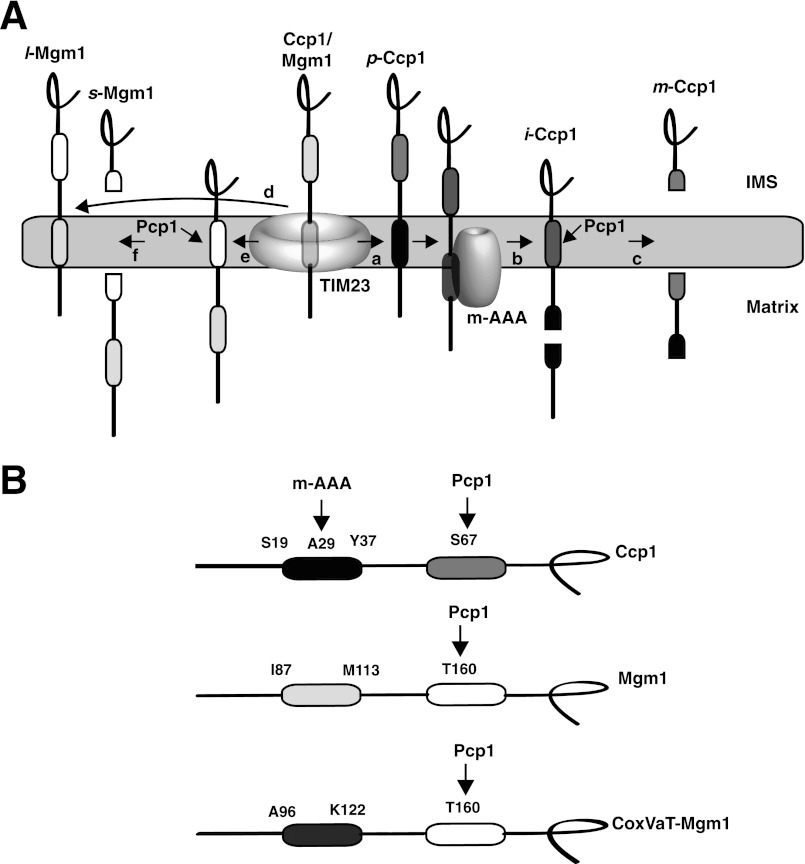
FIGURE 1.
A, maturation pathways for Ccp1 (right) and Mgm1 (left). The first hydrophobic segment (black) in p-Ccp1 triggers insertion from the TIM23 translocon into the inner membrane (arrow a). The membrane-integrated form is dislocated from the membrane and concomitantly cleaved in the middle of the hydrophobic segment by the inner membrane m-AAA protease complex, generating i-Ccp1 (arrow b). Finally, the rhomboid cleavage region (dark gray) in i-Ccp1 is cleaved by the rhomboid protease Pcp1 (arrow c), releasing m-Ccp1 in the intermembrane space (IMS) (8, 9). In the alternative topogenesis model for import of Mgm1 (11), the first hydrophobic segment integrates into the membrane in 30–40% of the molecules (arrow d), resulting in membrane-anchored l-Mgm1. For the remaining molecules, the first hydrophobic segment translocates into the matrix (arrow e), and the second hydrophobic segment is processed by Pcp1 (arrow f), generating s-Mgm1 in the intermembrane space (11). B, the model proteins Ccp1, Mgm1, and CoxVaT-Mgm1. The first hydrophobic segments of Ccp1 (Ser19–Tyr37), Mgm1 (Ile87–Met113), and CoxVaT-Mgm1 (Ala96–Lys122) were replaced with 19-residue H-segments with the composition GGPG(Leun/Ala19−n)GPGG. Pcp1 and m-AAA protease cleavage sites are indicated. In CoxVaT-Mgm1, residues 1–128 of CoxVa (shown in dark gray) are fused to residues 117–902 of Mgm1. Mgm1 H-segments and CoxVaT-Mgm1 H-segments carry a 3×HA tag in the C terminus.